
黄建华
与开放手术相比,腹主动脉腔内修复术(EVAR)已经彻底改变了腹主动脉瘤(AAA)的治疗策略,虽然腔内修复较开放手术二次干预率较开放手术更高,但是其在长期生存率(6年)方面没有明显差别[1],其手术死亡率和发病率低,住院时间短且出血量极少,已经成为现在世界上治疗AAA的主流手段。但是AAA中符合经典EVAR手术解剖标准的仅占总数的20%~50%[2-3]。瘤颈指的是肾动脉下方到病变AAA上部边界的相对正常血管,是支架锚定的关键区域,其长度直接决定着手术的风险和预后,是评估制定AAA手术方案和风险时最重要的参数之一[4-6]。以往的观点认为瘤颈短于15 mm者不主张行EVAR,原因是瘤颈越短,锚定区就越少,随之而来的术后并发症如I型内漏、移植物移位、肾动脉闭塞的可能性就越大[7-8]。随着耗材改进,手术水平的提高,适应证的部分限制逐渐被打破,部分超适应证患者不再是EVAR的绝对禁忌,短瘤颈AAA也同样如此,达到了令人满意的手术效果。Freyrie等[9]统计了4年间82例短瘤颈(长度<1 cm)的AAA患者,发现腔内治疗的近期和中期效果各项指标不亚于开放手术。下面就结合实际病例,简单介绍目前几种针对短瘤颈AAA的EVAR手段。
1 肾上固定技术
随着技术的发展,主动脉支架增加了头端倒钩以实现主动脉内的主动固定,而主动固定方式根据倒钩在肾动脉的相对位置又分为肾上和肾下固定,而肾上固定是目前应用较多的应对短瘤颈AAA的技术,主要以覆膜区近端有带倒钩的裸支架的产品如Zenith和Endurant支架来实现[10-11]。此种技术最大的好处就是依靠肾动脉上方的正常血管壁作为锚定区,充分利用了瘤颈,大大增加了短瘤颈AAA的手术适应证范围(图1A)。但有争议观点认为其可能增加肾脏缺血的风险,Boekler等[12]统计了663例EVAR发现,与肾下固定缺血比例为5.3%相比较,肾上固定的缺血比例是17.4%,其原因可能在于裸支架横跨肾动脉开口时,血液容易形成涡流导致。但也有Parmer等[13]统计认为,肾上固定与肾下固定相比,两组的近期、远期肾功能水平差异并没有统计学意义。
下面介绍1例短瘤颈肾上固定的病例:患者男,67岁,CTA显示其瘤颈很短,且合并瘤颈血栓。对该患者如果使用其他的技术强行在瘤颈处固定,一是锚定区长度不够,二是附壁血栓更加削弱了锚定的效果。笔者选择了Endurant腹主支架,裸区肾上固定,充分利用了瘤颈,可以看到固定效果满意,肾动脉开口位于支架裸区,血流没有受到影响。而且覆膜部分距离左肾动脉开口几乎只有1 mm,可谓是分毫不差(图1B)。
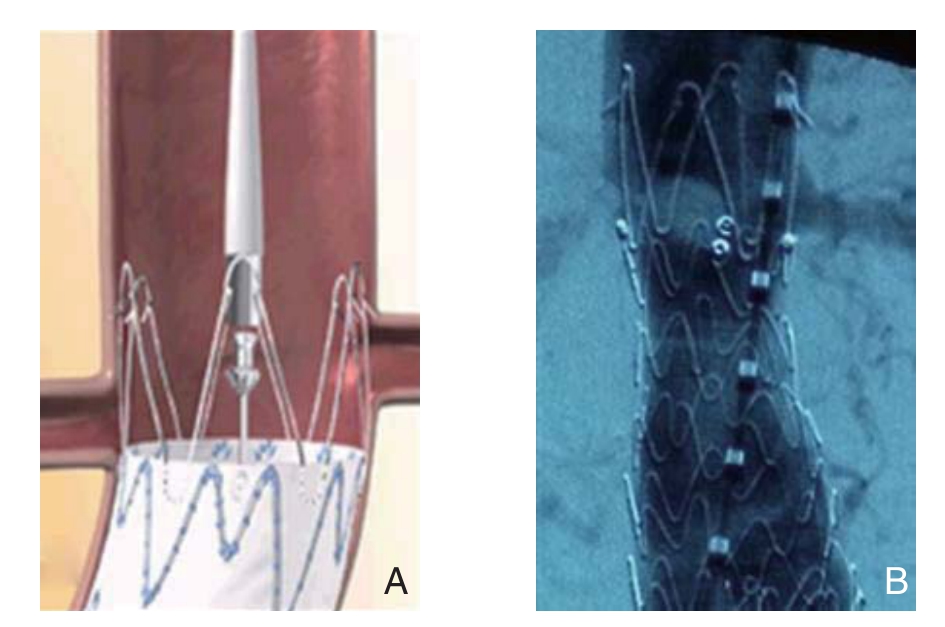
图1 肾上固定技术 A:肾上固定技术充分利用瘤颈;B:支架覆膜上端紧贴肾动脉下端
Figure 1 Suprarenal fi xation technique A: Making the utmost use of the aneurysmal neck; B: Tight adherence of the superior stent membrane to the inferior suprarenal artery
2 大支架支撑技术
某些AAA不仅瘤颈短,瘤颈形态更类似一个梯形,上窄下宽,这样如果用常规口径的支架,就算成功地固定在血管内部,也会因为实际的锚定区远远不够而导致支架掉落。大支架支撑技术是利用口径较大型号的覆膜支架,以梯形瘤颈的底边作为选择尺寸的依据,将梯形瘤颈撑开变为正常的形态。我们在实际工作中就碰到了这样的病例:患者男,67岁,瘤颈扭曲呈梯形,瘤颈仅为6 mm。根据测量其AAA参数,发现其瘤颈处呈近似梯形,下底边为18.8 mm。笔者选择了直径为28 mm的腹主动脉支架,最后手术的效果也令人满意(图2A)。另外1例患者,以急性发作腹痛4 d入院,行CTA检查发现其只有一侧左肾还被瘤体累及,而且AAA已经破裂形成了腹膜后血肿,急诊行EVAR术。术中试图将导丝选入肾动脉重建困难,由于手术时间紧急,故选择了首先用一体式支架在肾下先行解剖固定[14-15](将全程支撑一体化支架移植物骑跨在主-髂动脉分叉,再由髂动脉水平向肾动脉水平释放),再加入一个直筒式腹主动脉支架(裸支架部分在肾上)固定在一体式支架内。术后复查隔绝良好,无任何内漏(图2B)。
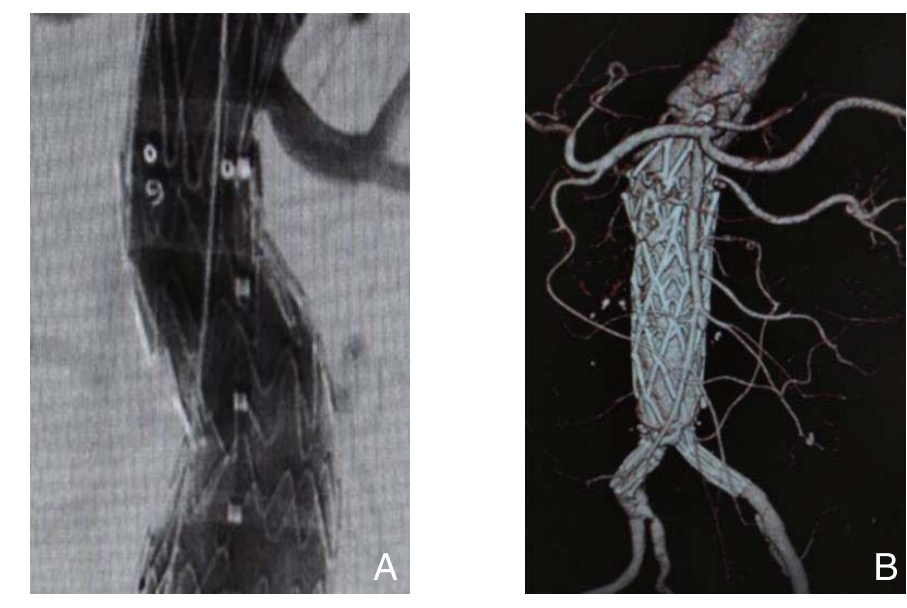
图2 大支架支撑技术 A:造影通畅无内漏;B:全程支撑一体化支架移植物骑跨在主-髂动脉分叉,解剖固定成功
Figure 2 Large-scaあ old technique A: Angiography showing patency of the artery and no endoleak; B: Whole course supporting unibody stent graft across the aorioiliac bifurcation, which indicating the successful anatomical fi xation
3 烟囱技术
烟囱技术是指在主动脉腔内移植物植入过程中,因手术需要必须覆盖重要分支时,在被覆盖的分支血管和近端主动脉之间应用裸支架或覆膜支架与主动脉移植物并排锚定,从而达到保全被覆盖分支血供的目的,因分支血管内支架的释放 位置形似烟囱而得名[16]。该技术主要用于肾动脉、肠系膜上动脉等内脏动脉分支被主动脉瘤完全累及时使用,也可以用作分支技术重建内脏动脉不成功时的补救措施[17]。基本步骤是在释放主体支架前导丝选入相应内脏动脉,置入覆膜支架后和主体支架平行。此项技术相对操作简单快捷,对器材要求不高,器材要求低,但一般认为其内漏率较高,远期通畅性不确定,内漏率随着烟囱支架数量增多上升,适用于AAA累及内脏动脉数量少特别是破裂型AAA(rAAA)的急诊腔内修复[18]。Li等[19]统计了2013—2014年12家血管外科中心236例AAA累及内脏分支接受烟囱技术治疗的患者,共置入335枚烟囱支架,发现30 d病死率为3.8%(9/236),随访期间I、II、III型内漏的发生率分别为11.8%(28/236)、8.1%(19/236)和0.4%(1/236)。下面的病例是1例老年女性,64岁,进行性加重腹痛3 d入院,查CTA示瘤体邻近右肾动脉,瘤颈短仅6 mm,紧接着便是巨大的瘤体,基本没有过渡,且AAA瘤体已经破裂。但是其左肾动脉离右肾动脉距离有8 mm左右,为了有效利用这8 mm的相对正常血管壁,笔者决定以覆膜支架带膜部分覆盖右肾动脉以保证充足的锚定区,同时以烟囱支架重建右肾动脉。术后1周复查CTA,结果示AAA成功隔绝,肾动脉通畅(图3)。
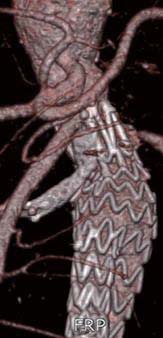
图3 烟囱支架成功重建右肾动脉,造影通畅
Figure 3 Successful reconstruction of the right renal artery with a chimney stent graft and graft patency by angiography
4 开窗(分支支架)技术
开窗型支架最早应用于1999年,以Cook公司的Zenith支架系统为代表。基本原理和操作步骤可以简单概括为:预先开窗,选入目标分支,释放分支支架[20]。此种技术适用于双肾动脉甚至是肠系膜上动脉等其他内脏动脉同时受累及的情况,其他技术均无法达到重建内脏动脉保留功能的情况下[7]。下面这个患者双肾动脉上下距离只有2 mm,右肾动脉离瘤体也只有不到4 mm,所以双肾动脉势必会被覆盖。我们首先考虑使用分支支架技术,但其存在几个弊端:费用高(数十万元)、周期长(厂家定制支架需要长达1个月)、厂商选择单一(目前只有Cook公司的Zenith支架)技术要求高、操作时间长等。经过探讨笔者最终选择首先在体外对照3D打印的患者腹主动脉模型精确地对Endurant支架预开窗,然后在手术中首先将导丝预置入双肾动脉,然后释放支架主体,造影显示双肾动脉显影良好(图4A)以后撤除预置肾动脉导丝,再从肱动脉置入肾动脉导丝,置入肾动脉支架后球囊扩张支架开口处使其与主体支架紧密结合,手术成功。
开窗腔内修复技术相比常规腔内修复手术应用时间较短,但安全性、远期效果有待时间验证。一项前瞻性研究随访了458例开窗修复术发现,在经验丰富的中心进行开窗修复手术是安全可靠的,其术后病死率和常规腔内修复术类似[21]。另外,在针对多个分支如双肾、肠系膜上动脉甚至腹腔干都受累,一味地追求完全分支支架解决耗时太长、耗费太高的情况下,还可以灵活运用开窗+开槽+分支支架结合的技术(图4B),以更经济高效地解决问题。胡忠洲等[22]为15例患有近肾AAA的患者采用定制Zenith开窗支架进行腔内修复术,共29处开窗和9处开槽,随访期间分支血管通畅率为100%,因此认为早中期结果显示采用定制Zenith开窗支架修复近肾AAA安全有效。
目前,血管外科学界有多种技术可以适用于腔内修复短瘤颈的AAA,并且随着新技术、新材料的层出不穷,短瘤颈已经很大程度上不再是AAA腔内修复的禁忌[23]。例如Endurant支架在不管在常规或异常瘤颈的患者都获得了令人满意的5年随访结果[24],另外Melas等[25]报道了Endologix的AFX支架移植物的初步经验,该技术是一种带STRATA技术的新装置,该装置可通过“活性”封闭自主贴附动脉壁缝隙以增强瘤颈固定,达到减少I型内漏的目的(图4C)。另外,血管外科医师在制定手术方案时应该考虑到患者的病情、经济情况,同时也要根据医院的硬件条件和医师的技术水平来合理选择适合的腔内修复方式。随着技术和器材的不断进步,有理由展望更多更复杂瘤颈的AAA,特别是短瘤颈合并扭曲瘤颈的AAA最终可以实现完全腔内修复。
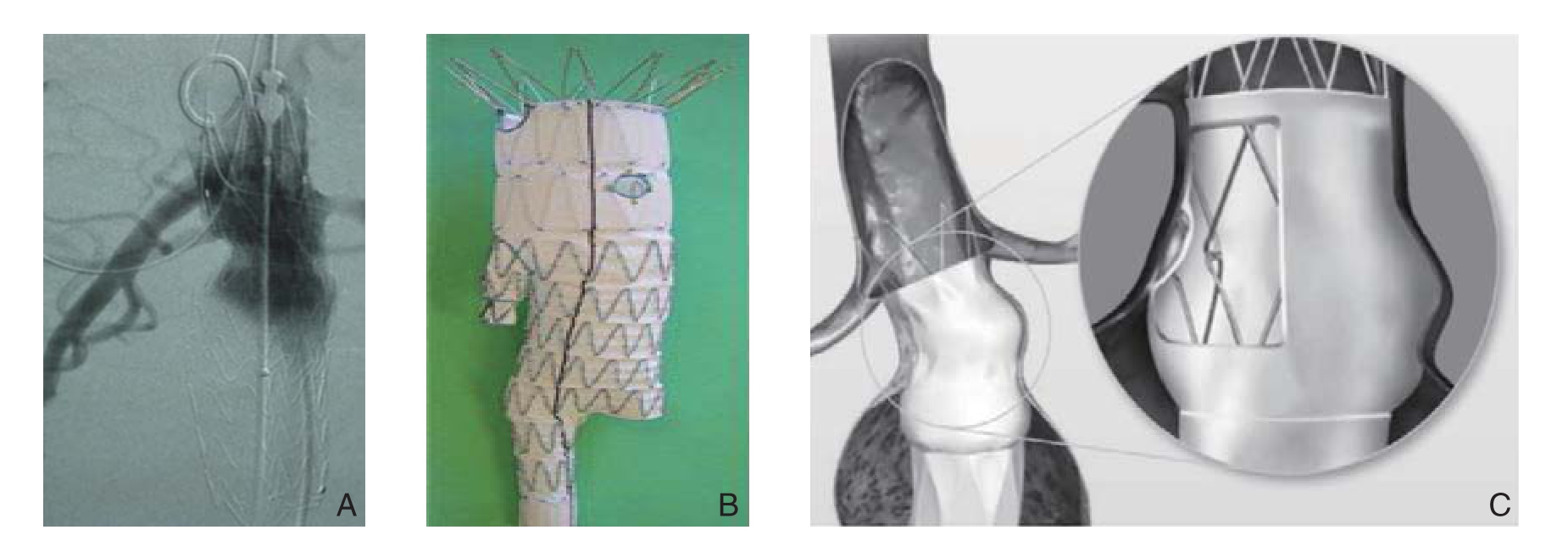
图4 开窗(分支支架)技术相关图片 A:Endurant支架预开窗术中导丝选入双肾动脉;B:开槽支架示意图;C:应用STRATA技术的AFX支架,可自主封闭贴合缝隙
Figure 4 Pictures associated with fenestration (bifurcated stent) techniques A: Introduction of the guiding wire into bilateral renal arteries during pre-fenestration with Endurant stent graft; B: Slotted Stents; C: AFX bifurcated stent graft based on STRATA technology, with the advantage of automatic closure and sealing of the spaces
参考文献
[1] De Bruin JL, Baas A F, Buth J, et al. Long-term outcome of open or endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm[J]. N Engl J Med, 2010, 362(20):1881-1889. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0909499.
[2] Elkouri S, Martelli E, Gloviczki P, et al. Most patients with abdominal aortic aneurysm are not suitable for endovascular repair using currently approved bifurcated stent-grafts[J].Vasc Endovascular Surg, 2004, 38(5):401-412. doi:10.1177/153857440403800502.
[3] Schanzer A, Greenberg RK, Hevelone N, et al. Predictors of abdominal aortic aneurysm sac enlargement after endovascular repair[J]. Circulation, 2011, 123(24):2848-2855. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.014902.
[4] Morrison TM, Meyer CA, Fillinger MF, et al. Eligiblity for Endovascular Repair of Short Neck Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms[J]. J Vasc Surg, 2013, 57(5 Suppl):24S. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2013.02.078.
[5] Lee JT, Ullery BW, Zarins CK, et al. EVAR deployment in anatomically challenging necks outside the IFU[J]. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg, 2013, 46(1):65-73. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2013.03.027.
[6] Galiñanes EL, Hernandez E, Krajcer Z. Preliminary results of adjunctive use of endoanchors in the treatment of short neck and pararenal abdominal aortic aneurysms[J]. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv, 2016, 87(4):E154-159. doi: 10.1002/ccd.26351.
[7] Dijkstra ML, Tielliu IF, Meerwaldt R, et al. Dutch experience with the fenestrated Anaconda endograft for short-neck infrarenal and juxtarenal abdominal aortic aneurysm repair[J]. J Vasc Surg, 2014,60(2):301-307. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2014.02.011.
[8] Bisdas T, Weiss K, Eisenack M, et al. Durability of the Endurant stent graft in patients undergoing endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair[J]. J Vasc Surg, 2014, 60(5):1125-1131.doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2014.04.070.
[9] Freyrie A, Gargiulo M, Gallitto E, et al. Abdominal aortic aneurysms with short proximal neck: comparison between standard endograft and open repair[J]. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino), 2012,53(5):617-623.
[10] 陈忠. 腹主动脉瘤腔内修复术中肾上与肾下固定的选择[J]. 血管与腔内血管外科杂志, 2015, 1(2/3):77-79. doi:10.19418/j.cnki.issn2096-0646.2015.z1.001.Chen Z. Selection of suprarenal and infrarenal fixation during endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurym[J]. Journal of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery, 2015, 1(2/3):77-79.doi:10.19418/j.cnki.issn2096-0646.2015.z1.001.
[11] 查斌山, 朱化刚, 谢文涛, 等. 短瘤颈和扭曲瘤颈的腹主动脉瘤腔内治疗[J]. 中华普通外科杂志, 2017, 32(4):361-362.
doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-631X.2017.04.025.Zha BS, Zhu HG, Xie WT, et al. Endovascular treatment of abdominal aortic aneurym with short or tortuous neck[J]. Zhong Hua Pu Tong Wai Ke Za Zhi, 2017, 32(4):361-362.doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-631X.2017.04.025.
[12] Böckler D, Krauss M, Mansmann U, et al. Incidence of renal infarctions after endovascular AAA repair: relationship to infrarenal versus suprarenal fi xation[J]. J Endovasc Ther, 2003, 10(6):1054-1060. doi: 10.1177/152660280301000605
[13] Parmer SS, Carpenter JP, Endologix Investigators. Endovascular aneurysm repair with suprarenal vs infrarenal fixation: a study of renal effects[J]. J Vasc Surg, 2006, 43(1):19-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2005.09.025.
[14] 张彦舫, 孔健, 窦永充, 等. 一体式覆膜支架的解剖固定方式在腹主动脉瘤血管腔内治疗中的应用[J]. 上海医学, 2014, 37(1):69-72.Zhang YF, Kong J, Dou YC, et al. Anatomical fixation.,endovascular unibody stent graft for abdominal aortic aneurysm[J].Shanghai Medical Journal, 2014, 37(1):69-72.
[15] 柏骏. “解剖固定”理论在AegisTM覆膜支架治疗腹主动脉瘤中的应用及中远期疗效评估[D]. 上海: 第二军医大学, 2013.Bai J. Application of anatomical fixation theory in the treatment of AAA with AegisTM stent-graft and its long-term efficacy assessment[D]. Shanghai: Second Military Medical University,2013.
[16] Hogendoorn W, Schlösser FJ, Moll FL, et al. Thoracic endovascular aortic repair with the chimney graft technique[J]. J Vasc Surg, 2013,58(2):502-511. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2013.03.043.
[17] Scali ST, Feezor RJ, Chang CK, et al. Critical analysis of results after chimney endovascular aortic aneurysm repair raises cause for concern[J]. J Vasc Surg, 2014, 60(4):865-873. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2014.03.295.
[18] Dias NV, Bin Jabr A, Sveinsson M, et al. Impact of renal chimney grafts on anatomical suitability for endovascular repair in ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm[J]. J Endovasc Ther, 2015, 22(1):105-109. doi: 10.1177/1526602814564384.
[19] Li Y, Zhang T, Guo W, et al. Endovascular chimney technique for juxtarenal abdominal aortic aneurysm: a systematic review using pooled analysis and meta-analysis[J]. Ann Vasc Surg, 2015,29(6):1141-1150. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2015.02.015.
[20] Harms J, Hess U, Cavallaro A, et al. The abdominal aortic fenestration procedure in acute thoraco-abdominal aortic dissection with aortic branch artery ischemia[J]. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino),1998, 39(3):273-280.
[21] Glebova NO, Selvarajah S, Orion KC, et al. Fenestrated endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms is associated with increased morbidity but comparable mortality with infrarenal endovascular aneurysm repair[J]. J Vasc Surg, 2015, 61(3):604-610.doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2014.10.025.
[22] 胡忠洲, 李悦, 郭伟, 等. 采用Zenith开窗支架腔内修复近肾腹主动脉瘤的临床研究[C]//2015国际血管联盟中国大会第十一届中国首都血管学术论坛论文汇编. 北京: 2015国际血管联盟中国大会第十一届中国首都血管学术论坛会议委员会, 2015.Hu ZZ, Li Y, Guo W, et al. Clinical study of endovascular repair of juxtarenal abdominal aortic aneurysm using Zenith fenestration stent graft[C]//Proceedings of the 2015 11th capital vascular academic forum of International vascular union China congress.Beijing: Committee of the 2015 11th capital vascular academic forum of International vascular union China congress, 2015.
[23] Troisi N, Torsello G. Commentary: new-generation devices and adjunctive procedures are the key elements to expanding the indications for endovascular aneurysm repair[J]. J Endovasc Ther,2015, 22(2):179-181. doi: 10.1177/1526602815575484.
[24] Troisi N, Torsello G, Weiss K, et al. Midterm results of endovascular aneurysm repair using the Endurant stent-graft according to the instructions for use vs. off-label conditions[J]. J Endovasc Ther,2014, 21(6):841-847. doi: 10.1583/14-4795MR.1.
[25] Melas N, Stavridis K, Saratzis A, et al. Active proximal sealing in the endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms: early results with a new stent-graft[J]. J Endovasc Ther, 2015, 22(2):174-178.doi: 10.1177/1526602815573232.