甲状腺乳头状癌(papillary thyroid carcinoma,PTC)是甲状腺癌最常见的病理类型,大约占所有甲状腺癌的80%~85%[1-2]。PTC是一种具有滤泡细胞分化及一系列核特征的上皮细胞恶性肿瘤。从临床发病率及预后来说,PTC是最常见的甲状腺肿瘤,同时也是总体预后最好的一种甲状腺恶性肿瘤。PTC通常表现为不规则的实性肿块,但在极少数情况下,可能具有囊性特征。PTC的主要特征之一是它能够侵入邻近结构,例如淋巴管。大约有10%的患者在最初被诊断时已经具有转移病灶,但对于年龄<45岁的患者来说,PTC的总体预后是较好的[3-5]。
甲状腺癌的预后受多种因素的调节。已有许多研究报道多种因素能影响甲状腺癌的发生、发展及转移,microRNA(miRNA)是其中一种重要因素。miRNA是一类由内源基因编码的长度约为18~25个核苷酸序列的小分子RNA,能通过结合到特定信使RNA的3'UTR来抑制基因的翻译或诱导降解,从而使其能够参与基因的转录后调控的过程。据文献[6-16]报道,miRNA发挥癌基因和抑癌基因的功能,参与细胞增殖、凋亡和分化的调控,在肿瘤的发生发展过程中具有重要作用。Chou等[17]研究表明miR-146b表达的失调与PTC侵袭与预后相关,因此可以作为一种新型的PTC生物标志物和治疗靶点。Minna等[18]研究表明miR-451a能作为抑癌基因并可以通过Akt/mTOR信号通路调节PTC的进展。
外泌体是一种由绝大多数细胞释放的、具有脂质双分子层和丰富内容物的微囊泡结构,直径约30~100 nm。近10年来发现外泌体中不仅包含功能性蛋白,还有功能性核酸物质,这些蛋白质、核酸对肿瘤的进展具有重要作用,成为肿瘤相关研究热点。
本研究通过提取低危复发风险和中高危复发风险PTC患者血清中的外泌体并通过microarray分析,筛选差异表达的miRNA,并以此为基础研究相关miRNA在调节PTC进展中的作用,并进一步探讨其内在信号通路。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料
1.1.1 细胞株 本研究中所使用PTC细胞TPC-1、K-1及293T细胞分别购于中南大学、上海中科院细胞库及ATCC 公司,由本实验室保存。
1.1.2 主要试剂 TRIzol™ Reagent、Lipofectamine™3000试剂购自Invitrogen公司;SYBR Green qPCR Mix、4×Reverse Transcription Master Mix均购自TaKaRa公司;8 μm Transwell小室、6孔盘、24 孔盘均购于美国Corning 公司;DMEM 培养基购于美国Invitrogen公司,胎牛血清购于美国Gibco公司;MAP2抗体、S100PBP抗体、CLDN18抗体、PRDX6、GAPDH抗体均购于美国Santa Cruz 公司。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 细胞培养 本实验所有细胞均在含10% 胎牛血清、1% 青霉素- 链霉素双抗、1% 谷氨酰胺的DMEM 培养基中培养,并置于5%CO2 的37℃细胞培养箱中培养。待细胞达到90% 以上密度时进行传代培养。
1.2.2 Transwell 侵袭实验 Transwell 侵袭实验使用8 μm Transwell 小室进行。先在上室加入100 μL经1:15~1:20 稀释的Matrigel胶,并置于37℃细胞培养箱中2 h 使其凝固;然后于上室加入150 L含50 000个细胞的无血清培养基,下室加入含血清的培养基,置于37℃细胞培养箱中培养12~24 h后,取出上室,进行清洗、固定、染色、显微镜下观察、拍照等。每组实验设置3个复孔。
1.2.3 qRT-PCR 实验 收集细胞后,PBS 洗涤2遍,离心取细胞沉淀,按照TRIzol™ Reagent 说明书提取细胞总RNA,依据4×ReverseTranscription Master Mix 试剂盒说明书将组织总RNA 逆转录为总cDNA,按照SYBR Green qPCR Mix 试剂盒说明书操作,以cDNA为模板,进行荧光定量PCR 反应。反应条件:94℃ 2 min,94℃ 20 s,60℃ 30 s,共40个循环。相关miRNA 引物序列如下:hsamiR-186-5p:5'-CAA AGA ATT CTC CTT TTG GGC T-3';hsa-miR-532-3p:5'-CCT CCC ACA CCC AAG GCT TGC A-3';hsa-miR-199b-3p:5'-ACA GTA GTC TGC ACA TTG GTT A-3';hsamiR-3158-5p:5'-CCT GCA GAG AGG AAG CCC TTC-3';hsa-miR-3605-5p:5'-TGA GGA TGG ATA GCA AGG AAG CC-3'。
1.2.4 Western blot 实验 待细胞生长到适宜量时,收取细胞,加入细胞裂解液提取蛋白,然后依次按电泳、转膜、封闭、洗膜、一抗孵育、洗膜、二抗孵育、洗膜、显影等步骤验证蛋白表达差异。
1.2.5 血清外泌体的提取及纯化 血清外泌体的提取及纯化所使用试剂盒为上海宇玫博生物科技有限公司血清外泌体提取试剂盒(UR52136),所有操作步骤严格按试剂盒说明进行。具体操作步骤详见公司官网试剂盒操作规程(http://www.umibio.cn/product/278182363)。
1.2.6 基因芯片分析及差异miRNA 筛选 收集了5 组确诊PTC患者血液标本,根据分化型甲状腺癌复发风险度分层(2015 版ATA 指南)为低危组(肿瘤无腺外侵犯、无淋巴结转移)和中高危组(肿瘤有腺外侵犯或有颈侧区淋巴结转移或中央区淋巴结转移超过5个),血液标本提取及纯化获得外泌体,然后将收集的外泌体进行芯片测序(华大基因公司),并通过测序热图结果筛选差异表达miRNA。同时收集了21 组确诊PTC患者的肿瘤组织标本,对差异表达的miRNA 进行验证。患者的选择及标本的收集均通过湖南省人民医院医学伦理委员会审批(审批号:2017 科研伦审第11号)。
1.2.7 miR-186-5p 过表达质粒的构建及抑制剂的信息 过表达 miR-186-5p 采用pLV 慢病毒质粒,序列(上游:CGC GTC AAA GAA TTC TCC TTT TGG GCT GTC GAC AGC CCA AAA GGA GAA TTC TTT GTT TTT G,下游:CGC AAA AAC AAA GAA TTC TCC TTT TGG GCT GTC GAC AGC CCA AAA GGA GAA TTC TTT G) 由Integrated DNA Technologies 公司提供。miR-186-5p 抑制剂(Thermo Fisher Scientific公司)瞬时转染:当细胞长至60%~80% 汇合度时转染,使用无血清DMEM 培养基稀释Lipofectamine™3000 试剂(无血清DMEM 培养基125 μL,Lipofectamine™3000试剂5 μL),使用无血清DMEM培基稀释DNA,制备DNA预混液,无血清DMEM培养基125 μL,抑制剂2.5 μg,在每管已稀释的Lipofectamine™3000 试剂中加入稀释的抑制剂(1:1),稀释的DNA 125 μL,稀释的Lipofectamine™3000 试剂125 μL,室温孵育10~15 min,加入DNA-脂质复合物至细胞中(每孔抑制剂-脂质体复合物250 μL,抑制剂量2 500 ng,Lipofectamine™3000 试剂用量5 μL);37℃孵育细胞2~4 d。然后分析转染细胞。
1.3 统计学处理
采用SPSS 22.0统计软件对本研究数据进行统计学分析,计量资料采用均数±标准差( ±s)表示,侵袭实验结果各组间差异比较采用t检验统计方法,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
±s)表示,侵袭实验结果各组间差异比较采用t检验统计方法,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结 果
2.1 不同复发风险PTC患者血清外泌体中差异表达的miRNA
提取5组低危复发风险与中高危复发风险PTC患者血清中的外泌体,并通过microarray分析两组之间差异表达的miRNA,结果显示,中高危复发风险PTC患者血清外泌体中4个miRNA(miR-186-5p、miR-532-3p、miR-199b-3p、miR-3158-5p)表达上调,1个miRNA(miR-3605-5p)表达下调(均P<0.05)(图1)。
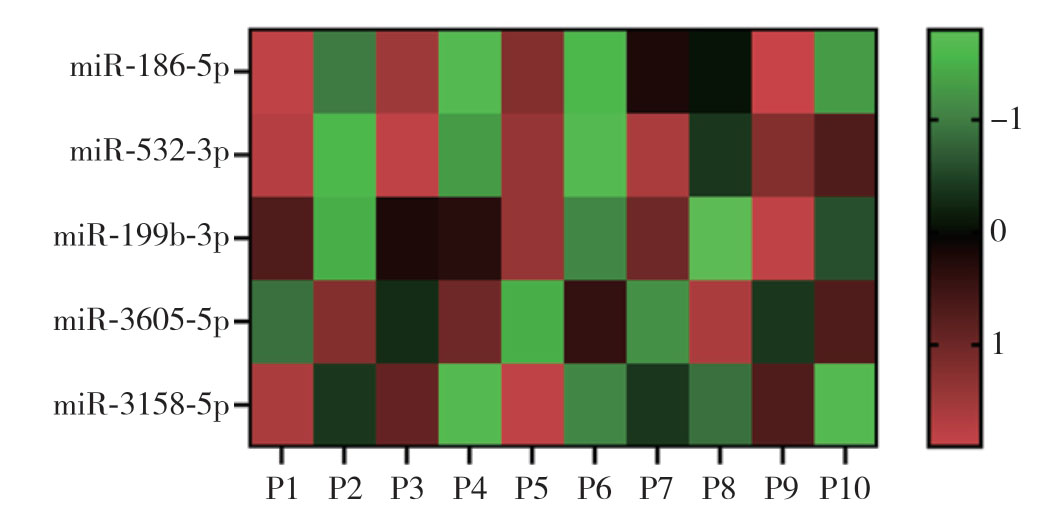
图1 microarray 分析PTC患者血清外泌体中差异表达的miRNA(P1、P3、P5、P7、P9为中高危复发风险PTC患者样本,P2、P4、P6、P8、P10为低危复发风险的PTC患者样本;红色表示表达升高,绿色表示表达降低)
Figure1 Microarray analysis of differentially expressed miRNAs in serum exosomes of PTC patients (P1,P3,P5,P7,P9:samples from PTC patients with intermediatehigh recurrence risk,P2,P4,P6,P8,P10:samples from PTC patients with low recurrence risk; red color standing for high expression,green color standing for low expression)
2.2 PTC患者癌组织中相关miRNA表达验证
通过qRT-PCR方法分别验证低危复发风险和中高危复发风险患者各21例PTC组织中上述5个miRNA表达情况,结果表明,miR-186-5p和miR-3158-5p在中高危复发风险患者的肿瘤组织中表达高于低危复发风险患者的PTC组织(均P<0.05)(图2)。
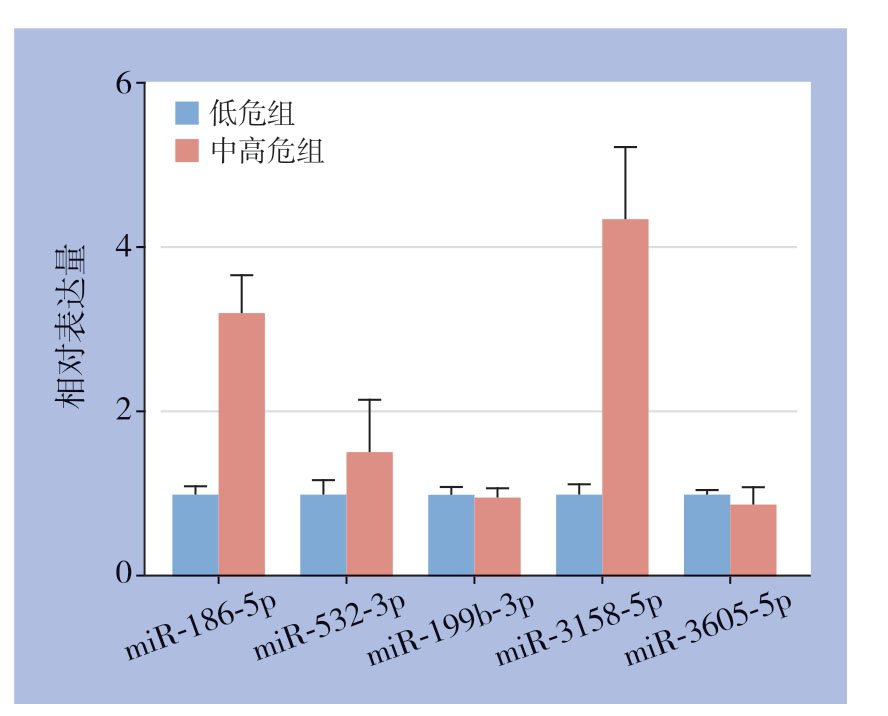
图2 qRT-PCR 验证PTC 组织中相关miRNA表达情况
Figure2 Expression of the related miRNAs in PTC tissues verified by qRT-PCR
2.3 miR-186-5p 与miR-3158-5p对PTC细胞的侵袭能力的影响
进一步在两种PTC细胞(TPC-1、K-1)中过表达miR-186-5p/miR-3158-5p或加入相应的miR-186-5p/miR-3158-5p抑制剂后检测PTC细胞侵袭能力,结果显示,过表达miR-186-5p能增加PTC细胞侵袭能力,加入mmiR-186-5p抑制剂能抑制PTC细胞的侵袭能力(均P<0.05),而miR-3158-5p的表达状态对PTC细胞的侵袭能力没有影响(均P>0.05)(图3)。
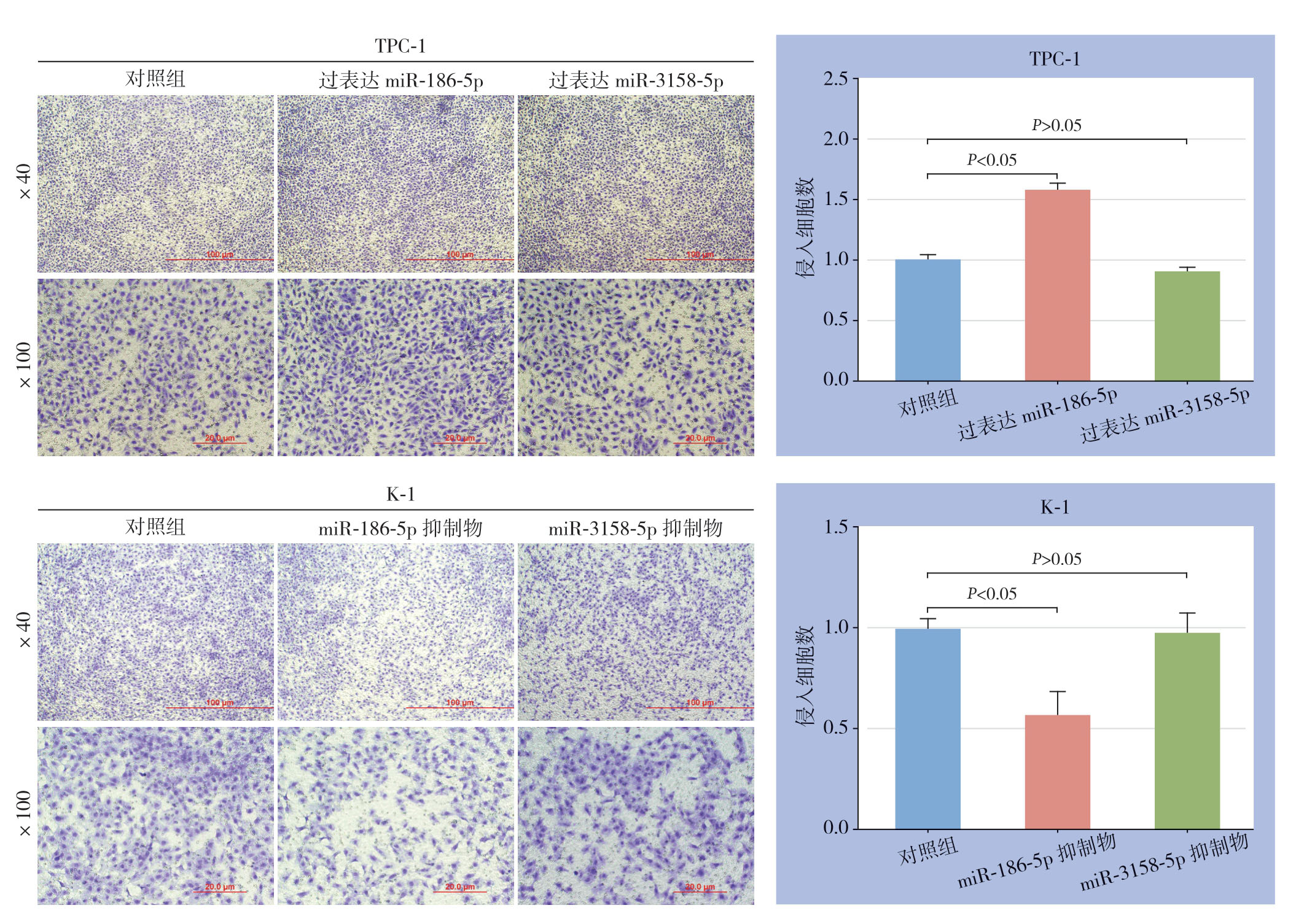
图3 不同miR-186-5p 或miR-3158-5p表达状态对PTC细胞侵袭能力的影响
Figure3 Influences of different expression statuses of miR-186-5p or miR-3158-5p on invasion ability of PTC cells
2.4 miR-186-5p 靶基因预测与鉴定
为了探讨miR-186-5p通过何种下游分子调控PTC细胞的侵袭能力,首先通过OncomiR在线数据库(http://www.oncomir.org/oncomir/search_target_miR.html)预测了miR-186-5p潜在作用的靶基因,结果显示,PRDX6、S100PBP、CLDN18、MAP2可能被miR-186-5p调控(图4)。进一步在PTC细胞中过表达miR-186-5p后检测PTC细胞中相应的蛋白表达情况,结果显示CLDN18表达下降,当加入miR-186-5p抑制剂时,CLDN18表达升高,而其他蛋白表达无明显变化(图5)。
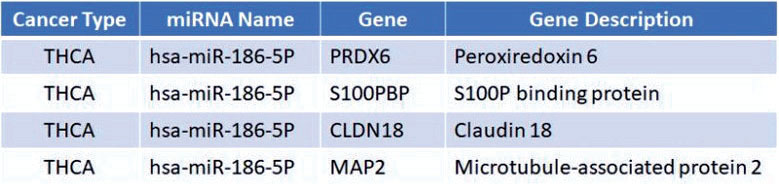
图4 OncomiR 在线数据库预测miR-186-5p 潜在靶基因
Figure4 Potential targets of miR-186-5p predicted through OncomiR database
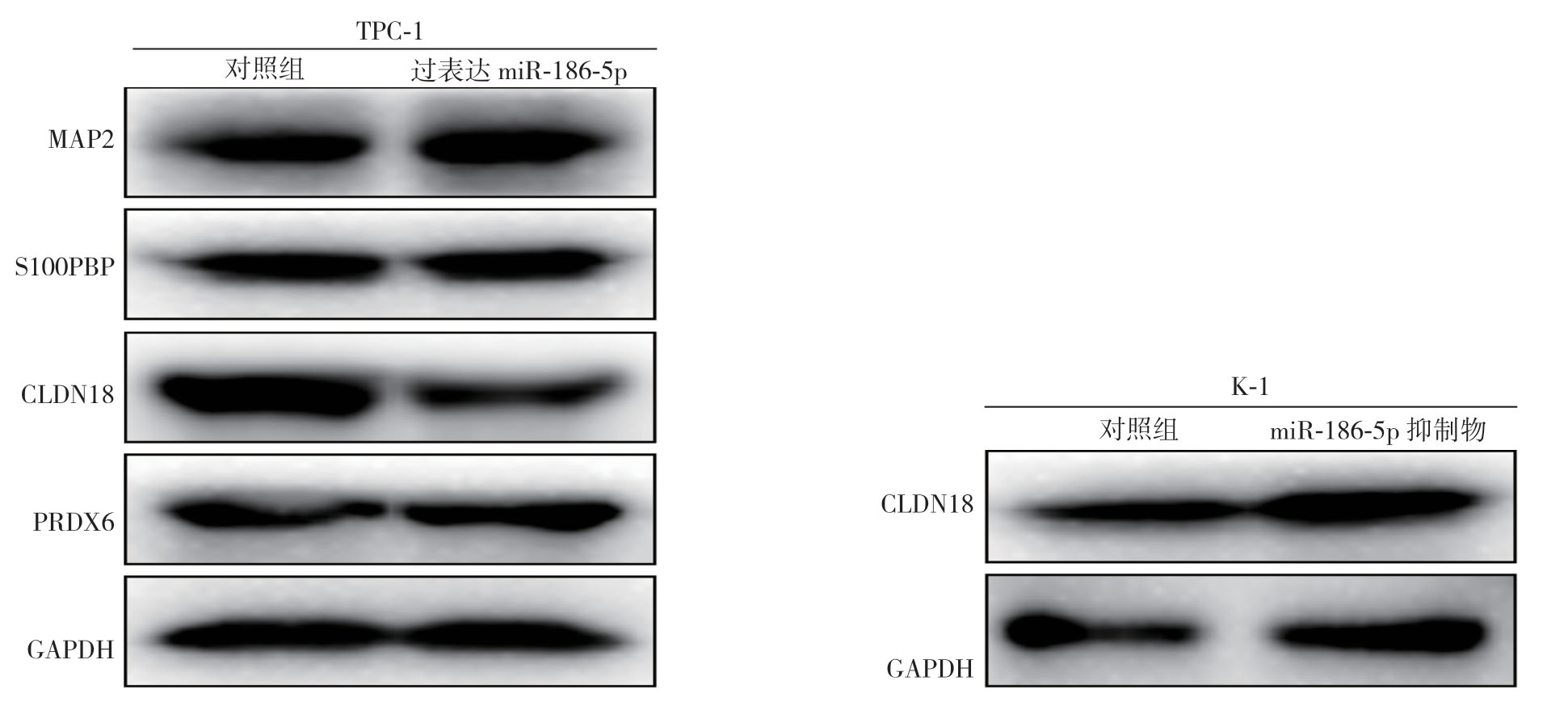
图5 过表达或敲低miR-186-5p 对PTC细胞相关基因蛋白表达的影响
Figure5 Influence of miR-186-5p overexpression and knock-down on protein expressions of the related genes
2.5 miR-186-5p 靶基因的功能分析与验证
侵袭能力实验结果显示,过表达CLDN18能抑制PTC细胞的侵袭,而敲低CLDN18能促进PTC细胞的侵袭能力(均P<0.05)(图6)。进一步逆转实验表明,过表达或敲低miR-186-5p对PTC细胞的作用被同时过表达或敲低CLDN18所逆转(均P<0.05)(图7)。使用GEPIA在线网站(http://gepia.cancer-pku.cn/index.html)分析TCGA数据库中PTC临床标本中CLDN18表达情况,结果显示与正常甲状腺组织相比,PTC肿瘤组织中CLDN18表达降低(图8),提示CLDN18可能是PTC的抑癌基因,这与其他肿瘤中相关报道一致[19]。
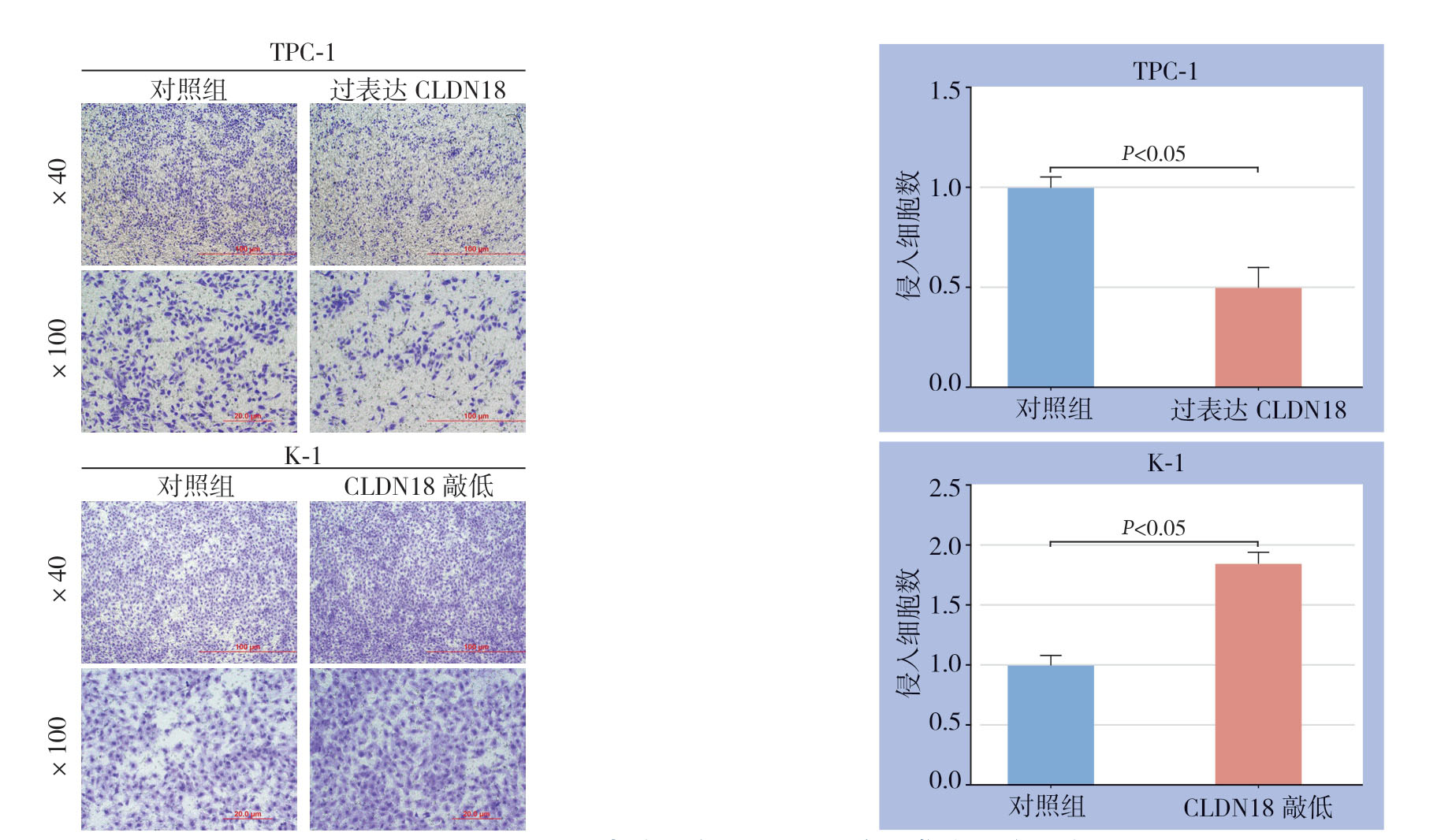
图6 不同CLDN18表达状态对PTC细胞侵袭能力的影响
Figure6 Influence of different CLDN18 status on invasion capacity of PTC cells

图7 CLDN18 对miR-186-5p 的逆转作用 A:miR-186-5p 抑制剂同时敲低CLDN18 或同时过表达miR-186-5p及CLDN18后PTC细胞侵袭能力的变化;B:miR-186-5p 抑制剂同时敲低CLDN18 或同时过表达miR-186-5p及CLDN18后PTC细胞相关蛋白表达的变化
Figure7 Reversal effects of CLDN18 on actions of miR-186-5p A:Change in invasion ability of PTC cells after miR-186-5p inhibitor treatment with simultaneous CLDN18 knock-down or both miR-186-5p and CLDN18 overexpression; B:Change in expressions of the relevant proteins in PTC cells after miR-186-5p inhibitor treatment with simultaneous CLDN18 knock-down or both miR-186-5p and CLDN18 overexpression
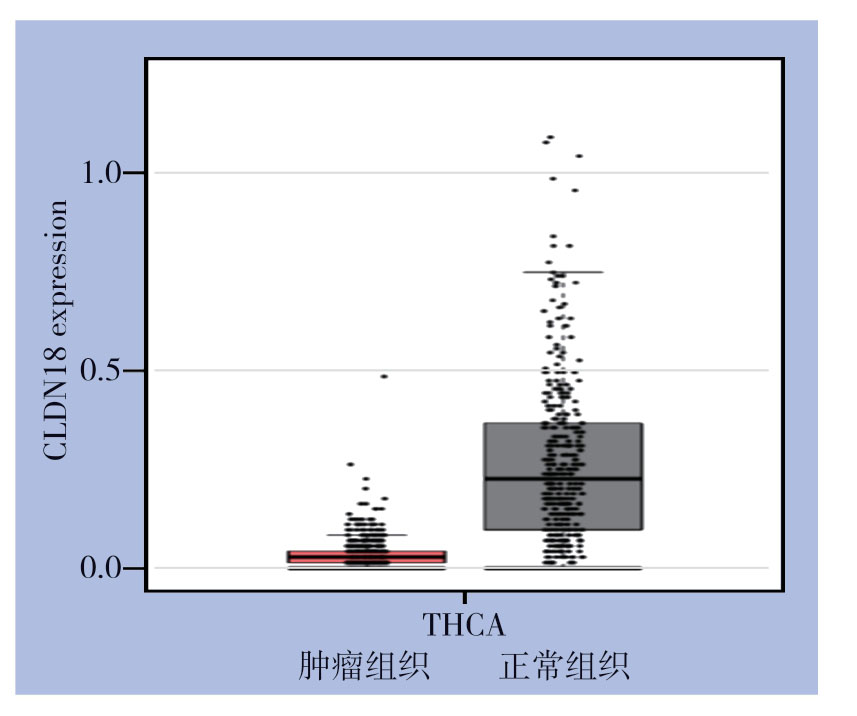
图8 GEPIA 数据库分析甲状腺肿瘤组织及正常组织中CLDN18表达情况
Figure8 Analysis of CLDN18 expression in thyroid tumor and normal tissue through GEPIA database
3 讨 论
甲状腺癌是源自内分泌系统的常见恶性肿瘤,根据流行病学调查显示,其发病率正在逐年上升[20-24]。根据美国流行病学调查显示,2020年预计新增甲状腺癌患者52 890例,同时预计将有新增死亡2 180例[24]。PTC是甲状腺癌最常见的病理类型,与其他恶性肿瘤相比,PTC预后较好,90%的PTC患者可以长期生存,但其复发率仍高达30%。虽然目前已经开发出了甲状腺乳头状癌的诊断和术后监测技术,但是由于诊断的阴性率以及相关干扰因素的存在,并且缺乏PTC预后的特定标志,使得PTC仍然是临床医生面临的难题。
miRNA是一种小的非编码RNA,能够通过切割靶信使RNA或抑制靶基因翻译的方式来抑制靶基因的表达[25]。近年的研究[26]表明miRNA可通过调控细胞增殖、凋亡和分化,促进或抑制肿瘤的恶性表型,相比正常细胞,肿瘤组织中miRNA存在明显异常表达,这些异常表达的miRNA在肿瘤形成中扮演重要角色,可作为肿瘤病因学、生物学特性、组织分型和临床分级分期的分子标志物。韦维等[27]研究表明,与人正常胃黏膜上皮细胞GES-1 比较,miR-124在各胃癌细胞中的表达均明显降低,进一步机制分析表明miR-124表达的下调可能通过激活PI3K/Akt信号通路来促进胃癌细胞的增殖、抑制其凋亡。Yoshizawa等[28]研究表明尿液外泌体中的miR-3940-5p/miR-8069比值可以作为胰腺导管腺癌的新型诊断生物标志物。Rashad等[29]研究表明血清miRNA-27a和miRNA-18b可作为丙型肝炎病毒相关肝细胞癌的潜在预测生物标志物。以此为基础,本研究通过检测PTC患者血清外泌体中miRNA含量,并通过芯片分析技术筛选出低危复发风险和中高危复发风险的PTC患者血清中差异表达的5个miRNA,然后将上述5个miRNA在临床组织标本中进一步分析,得出miR-186-5p可能在PTC侵袭及转移中发挥作用,并通过功能试验和逆转实验进一步证实miR-186-5p可以促进PTC的侵袭,从而进一步证实了miRNA在促进甲状腺乳头状癌的进展方面发挥重要作用。
miRNA能通过结合到特定信使RNA的3'UTR来抑制基因的翻译或诱导降解,从而使其能够参与基因的转录后调控的过程,以此实现对肿瘤的调节。本研究通过相关数据库分析并通过相关蛋白印迹、功能试验及逆转实验,得出miR-186-5p可通过调节下游CLDN18基因表达来促进PTC进展。CLDN18属于Claudin家族中的一员。Claudin是完整的膜蛋白,是紧密连接链的组成部分。紧密连接链可充当物理屏障,以防止溶质和水自由通过上皮或内皮细胞片之间的细胞旁空间,并且在维持细胞极性和信号转导中也起着关键作用。该基因在溃疡性结肠炎患者中上调,在浸润性导管腺癌中高度表达。PKC/MAPK/AP-1(蛋白激酶C/丝裂原活化蛋白激酶/激活蛋白-1)依赖性途径可调节该基因在胃细胞中的表达。CLDN18在不同肿瘤中发挥不同作用,可作为原癌基因/抑癌基因调节不同肿瘤的进展。Wan等[30]研究表明CLDN18可作为原癌基因促进肺腺癌细胞的生长、迁移及侵袭。Zhang等[19]研究表明CLDN18可作为抑癌基因抑制胃癌细胞的进展。本研究中miR-186-5p能抑制CLDN18基因的表达来促进PTC细胞的侵袭能力,进一步验证了CLDN18能作为抑癌基因来抑制PTC的进展。
综上所述,miR-186-5p在中高危复发风险PTC患者的血清外泌体及肿瘤组织中都表达升高,同时可以促进PTC细胞的侵袭能力,其表达状态可能与PTC的复发风险密切相关,其机制可能与抑制下游CLDN18基因表达有关。本研究结果可为PTC的诊断及基因治疗提供理论依据。
[1]Davies L,Welch HG.Increasing incidence of thyroid cancer in the United States,1973–2002[J].JAMA,2006,295(18):2164–2167.doi:10.1001/jama.295.18.2164.
[2]Casella C,Fusco M.Thyroid cancer[J].Epidemiol Prev,2004,28(2 Suppl):88–91.
[3]Morris L,Myssiorek D.Improved detection does not fully explain the rising incidence of well-differentiated thyroid cancer:a population-based analysis[J].Am J Surg,2010,200(4):454–461.doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2009.11.008.
[4]Davies L,Welch HG.Current thyroid cancer trends in the United States[J].JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg,2014,140(4):317–322.doi:10.1001/jamaoto.2014.1.
[5]La Vecchia C,Malvezzi M,Bosetti C,et al.Thyroid cancer mortality and incidence:a global overview[J].Int J Cancer,2015,136(9):2187–2195.doi:10.1002/ijc.29251.
[6]张雷,王宇锋,王亮,等.miR-105–5p在胃癌中的表达及其意义与生物学功能[J].中国普通外科杂志,2019,28(4):423–432.doi:10.7659/j.issn.1005–6947.2019.04.007.
Zhang L,Wang YF,Wang L,et al.Expression of miR-105–5p in gastric cancer and its significance and biological function[J].Chinese Journal of General Surgery,2019,28(4):423–432.doi:10.7659/j.issn.1005–6947.2019.04.007.
[7]谢黎明,张大利,贺荣芳.miR-124抑制胃癌MKN-45细胞的侵袭与转移[J].中国现代医生,2012,50(36):1–2.
Xie LM,Zhang DL,He RF.miR-124 inhibits the invasion and metastasis of gastric carcinoma MKN-45 cells[J].China Modern Doctor,2012,50(36):1–2.
[8]Verma S,Pandey M,Shukla GC,et al.Integrated analysis of miRNA landscape and cellular networking pathways in stagespecific prostate cancer.PLoS One.2019 Nov 22;14(11):e0224071.doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0224071.PMID:31756185; PMCID:PMC6874298.
[9]El Majzoub R,Fayyad-Kazan M,Nasr El Dine A,et al.A thiosemicarbazone derivative induces triple negative breast cancer cell apoptosis:possible role of miRNA-125a-5p and miRNA-181a-5p[J].Genes Genomics,2019,41(12):1431–1443.doi:10.1007/s13258–019–00866-y.
[10]Tong Z,Liu N,Lin L,et al.miR-125a-5p inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in colon cancer via targeting BCL2,BCL2L12 and MCL1[J].Biomed Pharmacother,2015,75:129–136.doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2015.07.036.
[11]Chen J,Chen Y,Chen Z.MiR-125a/b regulates the activation of cancer stem cells in paclitaxel-resistant colon cancer[J].Cancer Invest,2013,31(1):17–23.doi:10.3109/07357907.2012.743557.
[12]Li J,Zhang Y,Zhao J,et al.Overexpression of miR-22 reverses paclitaxel-induced chemoresistance through activation of PTEN signaling in p53-mutated colon cancer cells[J].Mol Cell Biochem,2011,357(1/2):31–38.doi:10.1007/s11010–011–0872–8.Epub 2011 May 19.PMID:21594648.
[13]Meng CY,Zhao ZQ,Bai R,et al.MicroRNA-22 mediates the cisplatin resistance of osteosarcoma cells by inhibiting autophagy via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway[J].Oncol Rep,2020,43(4):1169–1186.doi:10.3892/or.2020.7492.
[14]Zhou X,Natino D,Zhai X,et al.MicroRNA-22 inhibits the proliferation and migration,and increases the cisplatin sensitivity,of osteosarcoma cells[J].Mol Med Rep,2018,17(5):7209–7217.doi:10.3892/mmr.2018.8790.
[15]洪乐,肖卫东.microRNA调控胰腺癌干细胞的作用研究进展[J].中国普通外科杂志,2019,28(9):1137–1142.doi:10.3978/j.issn.1005–6947.2019.09.016.
Hong L,Xiao WD.Research progress of the role of microRNAs in regulating pancreatic cancer stem cells[J].Chinese Journal of General Surgery,2019,28(9):1137–1142.doi:10.3978/j.issn.1005–6947.2019.09.016.
[16]邓雪松,潘红艳,成俊,等.上调miR-449a表达对肝癌细胞生长和侵袭能力的影响[J].中国普通外科杂志,2018,27(1):68–74.doi:10.3978/j.issn.1005–6947.2018.01.011.
Deng XS,Pan HY,Cheng J,et al.Expression and action of miR-449a in hepatocellular carcinoma cells[J].Chinese Journal of General Surgery,2018,27(1):68–74.doi:10.3978/j.issn.1005–6947.2018.01.011.
[17]Chou CK,Liu RT,Kang HY.MicroRNA-146b:A Novel Biomarker and Therapeutic Target for Human Papillary Thyroid Cancer[J].Int J Mol Sci,2017,18(3):636.doi:10.3390/ijms18030636.
[18]Minna E,Romeo P,Dugo M,et al.miR-451a is underexpressed and targets AKT/mTOR pathway in papillary thyroid carcinoma[J].Oncotarget,2016,7(11):12731–12747.doi:10.18632/oncotarget.7262.
[19]Zhang SJ,Feng JF,Wang L,et al.miR-1303 targets claudin-18 gene to modulate proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer cells[J].Dig Dis Sci,2014,59(8):1754–1763.doi:10.1007/s10620–014–3107–5.
[20]Siegel RL,Miller KD,Jemal A.Cancer statistics,2016[J].CA Cancer J Clin,2016,66(1):7–30.doi:10.3322/caac.21332.
[21]Siegel RL,Miller KD,Jemal A.Cancer Statistics,2017[J].CA Cancer J Clin,2017,67(1):7–30.doi:10.3322/caac.21387.
[22]Siegel RL,Miller KD,Jemal A.Cancer statistics,2018[J].CA Cancer J Clin,2018,68(1):7–30.doi:10.3322/caac.21442.
[23]Siegel RL,Miller KD,Jemal A.Cancer statistics,2019[J].CA Cancer J Clin,2019,69(1):7–34.doi:10.3322/caac.21551.
[24]Siegel RL,Miller KD,Jemal A.Cancer statistics,2020[J].CA Cancer J Clin,2020,70(1):7–30.doi:10.3322/caac.21590.
[25]Ioriatti ES,Cirino MLA,Lizarte Neto FS,et al.Expression of circulating microRNAs as predictors of diagnosis and surgical outcome in patients with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy with hippocampal sclerosis[J].Epilepsy Res,2020,166:106373.doi:10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2020.106373.
[26]安娟,潘元明,康倩,等.胃癌患者血清miR-181d与PDCD4的表达及意义[J].肿瘤防治研究,2019,46(2):131–137.doi:10.3971/j.issn.1000–8578.2019.18.0486.
An J,Pan YM,Kang Q,et al.Expression and clinical signigicance of miR-181d and PDCD4 in serum of gastric cancer patients[J].Cancer Research on Prevention and Treatment,2019,46(2):131–137.doi:10.3971/j.issn.1000–8578.2019.18.0486.
[27]韦维,黄海舸,陆佳明,等.microRNA-124对胃癌细胞增殖与凋亡的影响及其与PI3K/Akt信号通路的关系[J].中国普通外科杂志,2020,29(6):723–730.doi:10.7659/j.issn.1005–6947.2020.06.013.
Wei W,Huang HG,Lu JM,et al.Effects of microRNA-124 on proliferation and apoptosis of gastric cancer cells and its relation with PI3K/Akt signaling pathway[J].Chinese Journal of General Surgery,2020,29(6):723–730.doi:10.7659/j.issn.1005–6947.2020.06.013.
[28]Yoshizawa N,Sugimoto K,Tameda M,et al.miR-3940–5p/miR-8069 ratio in urine exosomes is a novel diagnostic biomarker for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma[J].Oncol Lett,2020,19(4):2677–2684.doi:10.3892/ol.2020.11357.
[29]Rashad NM,El-Shal AS,Shalaby SM,et al.Serum miRNA-27a and miRNA-18b as potential predictive biomarkers of hepatitis C virusassociated hepatocellular carcinoma[J].Mol Cell Biochem,2018,447(1/2):125–136.doi:10.1007/s11010–018–3298–8.
[30]Wan YL,Dai HJ,Liu W,et al.miR-767–3p Inhibits Growth and Migration of Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells by Regulating CLDN18[J].Oncol Res,2018,26(4):637–644.doi:10.3727/096504 017X15112639918174.
