胆管癌起源于胆管上皮细胞,是严重危害人类健康的主要恶性肿瘤之一[1]。胆管癌起病隐匿,由于缺乏早期特异性及检查费用昂贵,因此胆管癌的早期诊断仍然是一大难题[2]。在全球范围内,胆管癌的发病率及病死率均呈上升趋势[3]。胆管癌的治疗以手术切除为首选方法,但手术切除率低,复发率高,术后生存率低[4-6],预后差。血清糖类抗原CA19-9(界点>129 U/mL)在本病诊断中有一些价值,但仍缺乏明确的血清肿瘤标志物[7]。已有研究表明,膜联蛋白A1(annexin A1)[8]、肝细胞生长因子(HGF)与其受体(C-Met)蛋白[9]、有丝分裂调控酶polo样激酶1(PLK1)和aurora A[10]、X连锁凋亡抑制蛋白(XIAP)[11]在胆管癌患者血清中高表达。随着血清肿瘤标志物研究的深入,相关种类逐渐被发现,敏感性、特异性的提升,在胆管癌诊治过程中,血清肿瘤标志物将会成为起决定性作用的成分之一[12]。血清肿瘤型M2丙酮酸激酶(tumor M2 pyruvate kinase,TuM2-PK)在胆汁中有较高灵敏度和特异度,可能会成为胆管癌新的肿瘤标志物,帮助诊断及判断预后[13]。近年来TuM2-PK在胃癌[14-16]、胰腺癌[17]、肺癌[18-19]及结直肠癌[20-21]恶性肿瘤标志物中的研究越来越多,已有研究发现TuM2-PK在胆管癌组织中高表达[22],本研究旨在探讨血清TuM2-PK在胆管癌诊断中的价值,为其临床应用提供依据。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选取2012年9月—2017年10月在中国人民解放军第二五一医院普通外科收治的54例胆管癌患者,其中,男31例,女23例;年龄38~82岁,中位年龄62岁,年龄>60岁者29例,年龄≤60岁者25例;经病理医师证实均为胆管腺癌,其中肿瘤≤2 cm者25例,肿瘤>2 cm者29例;上段胆管癌24例,中下段胆管癌30例;有神经侵犯者22例,无神经侵犯者32例;低分化腺癌34例,高中分化腺癌20例;有淋巴结转移者25例,无淋巴结转移者29例;I~II期38例,III~IV期16例。54例患者均行手术治疗,术前均未行放疗、化疗或免疫治疗等辅助治疗,其中根治性手术43例(肝门部胆管癌根治19例,根治性胰十二指肠切除术24例),姑息性手术11例(胆肠吻合6例,胆管T管引流术5例)。随机抽选同期住院胆管结石患者32例,男18例,女14例;年龄38~72岁。随机抽选同期行健康体检者25例为对照组,男15例,女10例;年龄36~75岁,均无肿瘤家族史。3组性别及年龄比例比较差异无统计学意义(均P>0.05)。
1.2 标本采集
因胆管癌术后平均住院时间为12 d,胆管结石术后平均住院时间为5 d,胆管癌组分别于术前及术后10 d清晨空腹静脉抽血约5 mL,胆管结石组分别于术前及术后3 d清晨空腹静脉抽血约5 mL,对照组抽取清晨空腹静脉血约5 mL,将静脉血置于抗凝管内,摇匀后经离心机3 500 r/min离心15 min后分离出血清,标记后存储于-80 ℃冰箱备用。
1.3 试剂与仪器
TuM2-PK采用酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)检测,人M2-PK ELISA试剂盒购自武汉伊莱瑞特生物科技股份有限公司,仪器为DNM-9602酶标分析仪(北京朗普新技术有限公司),严格按试剂说明书进行操作,以TuM2-PK>15 U/mL判断为阳性结果[23-25]。CA19-9采用化学发光法检测,仪器为美国贝克曼公司的XDI800,以CA19-9>37 U/mL判断为阳性结果。
1.4 统计学处理
采用SPSS 17.0软件进行统计分析,计量资料用均数±标准差(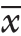 ±s)表示,计数资料以例和百分率表示,组间计量资料比较采用t检验,组间计数资料的比较采用χ2检验,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
±s)表示,计数资料以例和百分率表示,组间计量资料比较采用t检验,组间计数资料的比较采用χ2检验,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结 果
2.1 不同患者血清TuM2-PK水平比较分析
胆管癌患者血清TuM2-PK明显高于胆管结石患者和健康对照者,差异有统计学意义(均P<0.05);胆管结石患者与健康对照者间TuM2-PK水平差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)(表1)。
表1 各组血清TuM2-PK水平比较( ±s)
±s)
Table 1 Comparison of the serum TuM2-PK levels among groups ( ±s)
±s)
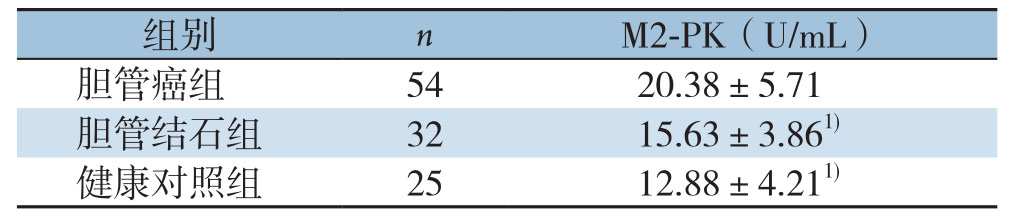
注:1)与胆管癌组比较,P<0.05
Note: 1) P<0.05 vs.cholangiocarcinoma group
images/BZ_102_1286_2151_2266_2200.pngimages/BZ_102_1286_2249_2266_2299.png胆管癌组 54 20.38±5.71健康对照组 25 12.88±4.211)
2.2 不同临床病理参数与胆管癌患者血清TuM2-PK阳性率的关系
胆管癌患者血清TuM2-PK阳性率与肿瘤的分化程度、淋巴结转移和TNM分期密切有关(均P<0.05),而与性别、年龄、肿瘤大小、肿瘤位置及有无神经侵犯无关(均P>0.05)(表2)。
表2 不同临床病理参数与胆管癌患者血清TuM2-PK阳性率的关系[n(%)]
Table 2 The relations of different clinicopathologic parameters with the positive rate of serum TuM2-PK in of cholangiocarcinoma patients [n (%)]
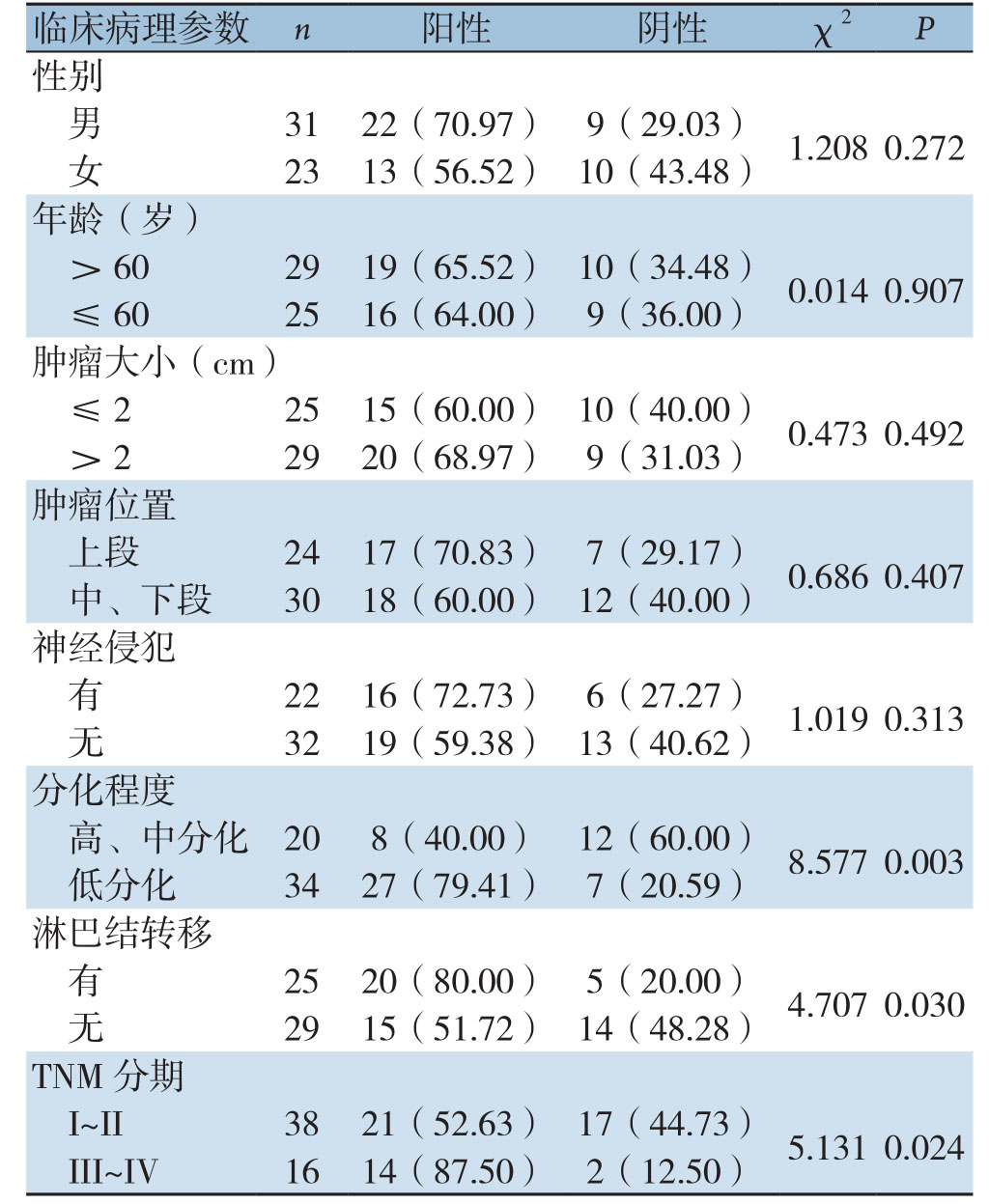
images/BZ_103_211_821_1191_1857.png临床病理参数 n 阳性 阴性 χ2 P性别男31 22(70.97) 9(29.03) 1.208 0.272女23 13(56.52) 10(43.48)
2.3 胆管癌患者血清TuM2-PK与CA19-9表达水平真实性与预测值分析
ROC曲线分析结果显示,血清TuM2-PK的曲线下面积值(AUC)为0.781(>0.5),且对于诊断胆管癌具有显著的意义(P=0.037)(图1)。血清TuM2-PK诊断胆管癌的灵敏度为84.81%(35/54)、特异度为80.00%(20/25)、阳性预测值为87.50%(35/40);血清CA19-9诊断胆管癌的灵敏度为79.63%(43/54)、特异度为84.00%(21/25)、阳性预测值为91.49%(43/47),血清TuM2-PK与CA19-9联合检测(两者任有一项为阳性计为阳性,同时为阴性计为阴性)灵敏度为96.91%、特异度为67.93%(表3-4)。与CA19-9检测相比,TuM2-PK检测胆管癌结果的灵敏度较高,特异度较低,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);与CA19-9单独检测相比,TuM2-PK+CA19-9的检测结果敏感度增高,但特异度降低。
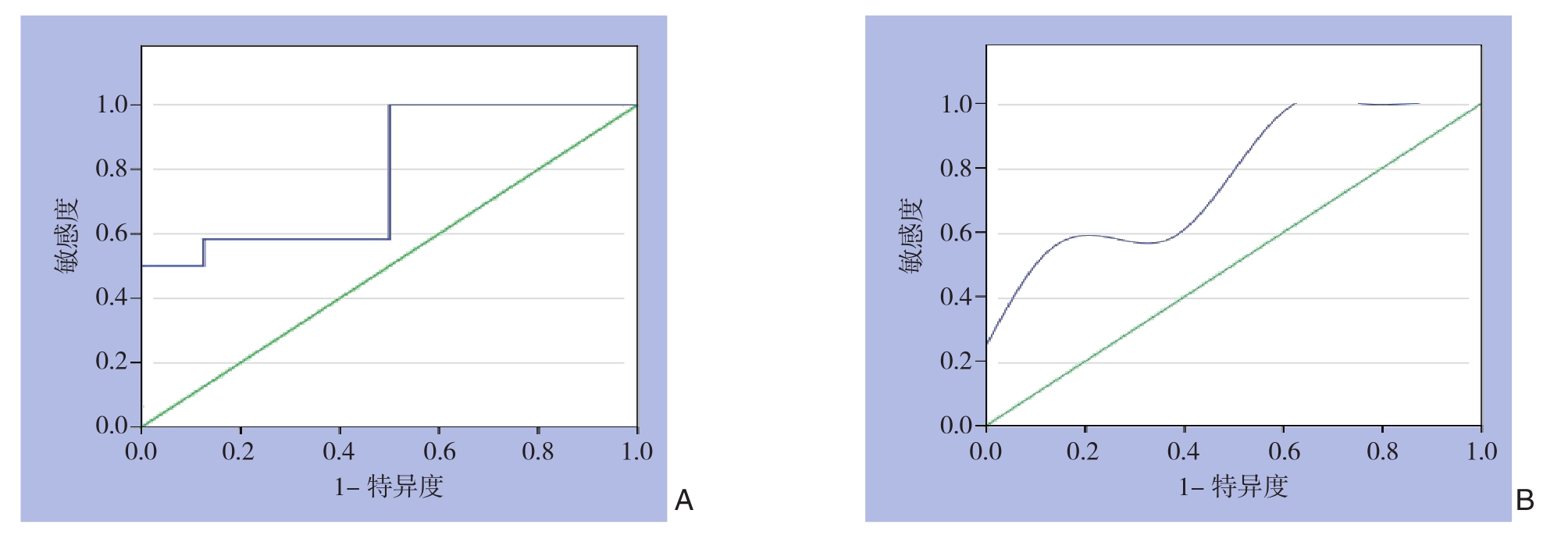
图1 血清TuM2-PK诊断胆管癌的ROC曲线 A:原始ROC曲线;B:调节后的ROC曲线
Figure 1 ROC curve of serum TuM2-PK for diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma A: Original ROC curve; B: Optimal ROC curve
表3 胆管癌患者血清TuM2-PK与CA19-9诊断效能比较
Table 3 Comparison of diagnostic efficiencies of serum TuM2-PK and CA19-9
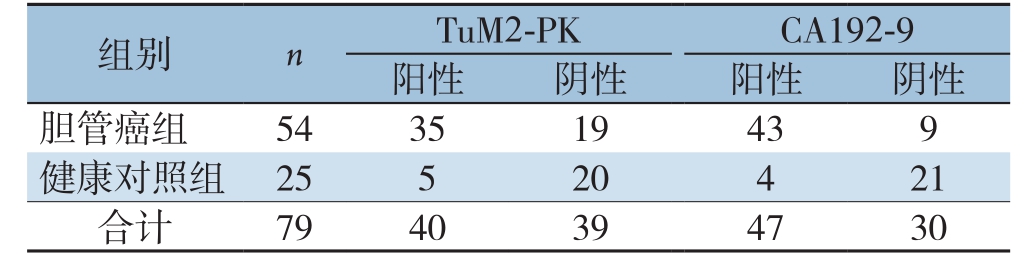
images/BZ_103_211_2955_1194_3054.pngimages/BZ_103_211_3103_1194_3153.png胆管癌组 54 35 19 43 9合计 79 40 39 47 30
表4 血清TuM2-PK与CA19-9单独及联合检测结果比较
Table 4 Comparison of results of lone and combined examination of serum TuM2-PK and CA19-9
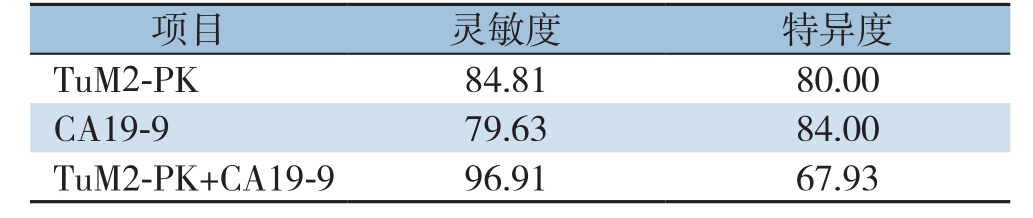
images/BZ_103_1286_2955_2266_3005.pngimages/BZ_103_1286_3054_2266_3103.pngT uM2-PK 84.81 80.00 TuM2-PK+CA19-9 96.91 67.93
2.4 胆管癌组及胆管良性病变组手术前后血清TuM2-PK水平变化
胆管癌组患者术前血清TuM2-P K水平为(20.38±5.71)U/mL,术后为(14.19±4.53)U/mL,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);胆管结石组患者术前血清TuM2-PK水平为(15.63±3.86)U/mL,术后为(14.45±3.23)U/mL,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。
2.5 根治性手术与姑息性手术者手术前后血清TuM2-PK水平变化
胆管癌患者中,根治性手术组患者术后血清TuM2-PK含量低于术前[(20.03±6.31)U/mL vs.(13.24±3.81)U/mL,P<0.05];姑息性手术组患者手术前后血清TuM2-PK含量的差异无统计学意义[(20.09±5.63)U/mL vs.(20.09±5.63)U/mL,P>0.05]。
3 讨 论
M2-PK是丙酮酸激酶的一种同工酶,在肿瘤组织中以与磷酸化丙酮酸低亲和力的二聚体形式优先表达,故又称为肿瘤型M2-PK[21]。研究报道M2-PK能够促进恶性肿瘤细胞的侵袭和转移,包括肝癌[26]、胃癌[27]、胰腺癌[28]、结直肠癌[29]等消化系肿瘤,并且指出M2-PK可作为预测癌症患者不良预后的独立因素。柴浩等[22]发现M2-PK在胆管癌组织中的表达明显高于癌旁组织,提示其在胆管癌的发生发展中发挥重要作用。
本研究发现,TuM2-PK在胆管癌患者血清水平明显高于胆管结石患者与健康对照者,胆管结石患者血清TuM2-PK水平虽然高于健康对照者,但差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),这说明确定好TuM2-PK的医学决定水平可用于区别胆管的恶性病变、良性病变及健康组织,这与Li等[30]报道的在胆管癌患者血清中TuM2-PK水平明显高于正常者及良性疾病患者的结果一致。
胆管癌患者TuM2-PK水平的表达与癌细胞的分化程度、肿瘤是否有淋巴结转移及临床病理TNM分期密切有关,而与患者性别、年龄、肿瘤大小、肿瘤位置及有无神经侵犯无关。癌细胞分化程度越低,血清中TuM2-PK阳性率水平就越高,有淋巴转移的患者比未发生淋巴转移的患者血清中TuM2-PK阳性率水平高。在临床病理TNM分期中,III~IV期患者血清中TuM2-PK阳性率水平显著高于I~II期患者。这些结果都明确表明了胆管癌患者血清TuM2-PK水平变化随着癌细胞生物状态的改变而改变,一定程度上反映了肿瘤的发生、发展。
本研究发现,血清TuM2-PK诊断胆管癌的灵敏度高于CA19-9,但特异度低于CA19-9,这表明TuM2-PK相对于CA19-9在临床诊断胆管癌方面具有更高的检出率。目前肿瘤标志物的联合检测是研究的一大热点,在肿瘤预防、诊断和预后中肿瘤标志物将会占有很重要的地位[31]。有研究表明,对于胃癌患者[14,16,32],肺癌患者[18-19],结肠癌患者[33]通过TuM2-PK与其它肿瘤标志物联合检测,能够进一步提高诊断的灵敏度与特异度。本研究亦发现,通过血清TuM2-PK与CA19-9联合检测,灵敏度为96.91%、特异度为67.93%,灵敏度均明显高于单纯TuM2-PK或CA19-9检查,但特异度降低,可能在提高误诊率,降低漏诊率的同时,会增加患者的医疗成本。
本研究中的5 4例胆管癌患者手术后血清TuM2-PK水平明显低于手术前,其中肿瘤切除的患者术后血清TuM2-PK明显降低,但肿瘤未切除的姑息性手术患者手术前后血清TuM2-PK的差别不明显,考虑由于肿瘤仍存在,导致血清TuM2-PK水平无明显改变。由此笔者推测血清TuM2-PK可作为胆管癌术前诊断、术后效果及肿瘤转移复发的评价指标。
目前,手术切除仍是治疗胆管癌的首要方法,化疗药物敏感性差,且临床药物治疗过程中易出现抗药性[34],如何从分子水平上对胆管癌的发生、发展情况进行分析,并采取有效的基因靶向治疗则是肿瘤化疗的新方向[35]。在胃癌的研究中发现,缺氧诱导因子(HIF-1α、HIF-2α)均可调控TuM2-PK的表达[36],二烯丙基二硫可能通过靶向TuM2-PK抑制胃癌细胞能量代谢[37],let-7a是通过调控PKM2的表达水平从而抑制胃癌细胞生长[38],笔者认为TuM2-PK作为肿瘤治疗的新靶点,为抗肿瘤的药物研发、肿瘤的预后提供了新策略。
本次研究选取样本较小,对照组选取随机,可能不能反映真实情况,但是目前国内外对TuM2-PK在胆管癌血清中的表达报道较少,本次研究获取了一定的试验数据,如能加大样本量,进行多中心前瞻性大规模的病例对照研究,取得更为精确和可信的数据值,将有助于提高TuM2-PK的临床应用价值。
胆管癌患者血清TuM2-PK水平可在一定程度上代表癌细胞的生物学状态,反映了胆管癌的发生、发展。血清TuM2-PK检测能够作为临床早期诊断胆管癌,判断临床分析,评估治疗预后的重要指标,与CA19-9联合检测能够进一步提高胆管癌的临床检出率。
[1] Sribenja S, Natthasirikul N, Vaeteewoottacharn K, et al.Thymosin β10 as a predictive biomarker of response to 5-fluorouracil chemotherapy in cholangiocarcinoma[J].Ann Hepatol, 2016,15(4):577-585.doi: 10.5604/16652681.1203155.
[2] Jiang L, Tan H, Panje CM, et al.Role of 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma[J].Clin Nucl Med, 2016,41(1):1-7.doi: 10.1097/RLU.0000000000000998.
[3] Kaewpitoon SJ, Rujirakul R, Loyd RA, et al.Surveillance of Populations at Risk of Cholangiocarcinoma Development in Rural Communities of Thailand Using the Korat-CCA Verbal Screening Test[J].Asian Pac JCancer Prev, 2016, 17(4):2205-2209.doi:10.7314/apjcp.2016.17.4.2205.
[4] 晏益核, 黄玉斌, 蔡小勇.肝门部胆管癌的外科治疗现状[J].中国普通外科杂志, 2017, 26(2):246-251.doi:10.3978/j.issn.1005-6947.2017.02.019.Yan YH, Huang YB, Cai XY.Current status in surgical management of hilar holangiocarcinoma[J].Chinese Journal of General Surgery,2017, 26(2):246-251.doi:10.3978/j.issn.1005-6947.2017.02.019.
[5] 项灿宏, 童翾.肝门部胆管癌外科治疗的进展与争议[J].中国普通外科杂志, 2018, 27(2):137-142.doi:10.3978/j.issn.1005-6947.2018.02.001.Xiang CH, Tong X.Surgical treatment of hilar cholangiocarcinoma:progress and controversy[J].Chinese Journal of General Surgery,2018, 27(2):137-142.doi:10.3978/j.issn.1005-6947.2018.02.001.
[6] 李薇, 杨芸, 宋富强, 等.体外共培养体系中胆管癌细胞对人脐静脉内皮细胞b-FGF和VEGF表达的影响[J].重庆医学, 2015,44(13):1749-1751.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-8348.2015.13.008.Li W, Yang Y, Song FQ, et al.Influence of cholangiocarcinoma cell lines on expression of b-FGF and VEGF in HUVEC in a coculture system[J].Chongqing Medicine, 2015, 44(13):1749-1751.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-8348.2015.13.008.
[7] 房龙, 樊艳华.《2016年欧洲肿瘤内科学会胆管癌诊断、治疗与随访临床实践指南》摘译[J].临床肝胆病杂志, 2017, 33(2):238-243.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2017.02.005.Fang L, Fan YH.An excerpt of 2016 ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up in biliary cancer[J].Journal of Clinical Hepatology, 2017, 33(2):238-243.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2017.02.005.
[8] 李辽, 王金, 尚培中.膜联蛋白A1和CA19-9在胆管癌中的表达及其临床意义[J].中国现代医学杂志, 2016, 26(10):31-35.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1005-8982.2016.10.007.Li L, Wang J, Shang PZ.Expressions of Annexin A1 and CA19-9 in cholangiocarcinoma and their clinicopathological significance[J].China Journal of Modern Medicine, 2016, 26(10):31-35.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1005-8982.2016.10.007.
[9] 王金, 赵一洁, 崔广宾, 等.HGF蛋白与C-Met蛋白在胆管癌中的表达及临床意义[J].重庆医学, 2016, 45(17):2362-2364.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-8348.2016.17.019.Wang J, Zhao YJ, Cui GB, et al.Expression and clinical significance of HGF and C-Met in cholangiocarcinoma[J].Chongqing Medical Journal, 2016, 45(17):2362-2364.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8348.2016.17.019.
[10] 崔学振, 尚培中.肝外胆管癌患者癌组织与血清中PLK1、Aurora A水平的变化及其临床意义[J].中国普通外科杂志, 2016,25(8):1151-1157.doi:10.3978/j.issn.1005-6947.2016.08.011.Cui XZ, Shang PZ.Changes in PLK1 and Aurora A levels in tumor tissue and serum of patients with extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and their clinical significance[J].Chinese Journal of General Surgery, 2016, 25(8):1151-1157.doi:10.3978/j.issn.1005-6947.2016.08.011.
[11] 陈雷, 尚培中.胆管癌患者癌组织与血清中XIAP、SMAC水平的变化及其临床意义[J].中国普通外科杂志, 2016, 25(9):1296-1301.doi:10.3978/j.issn.1005-6947.2016.09.012.Chen L, Shang PZ.Changes in XIAP and SMAC levels in tumor tissue and serum of patients with cholangiocarcinoma and their clinical significance[J].Chinese Journal of General Surgery, 2016,25(9):1296-1301.doi:10.3978/j.issn.1005-6947.2016.09.012.
[12] 赵福英, 余芃, 邓友松, 等.胆管癌血清肿瘤标志物及临床意义[J].检验医学与临床, 2016, 13(21):3114-3116.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-9455.2016.21.054.Zhao FY, Yu F, Deng YS, et al.Serum tumor markers for cholangiocarcinoma and their clinical significance[J].Laboratory Medicine and Clinic, 2016, 13(21):3114-3116.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-9455.2016.21.054.
[13] 马晓霖, 陈建平.肝门部胆管癌诊断技术的新进展[J].临床肿瘤学杂志, 2015, 20(8):760-764.Ma XL, Chen JP.New progress of the diagnosis technology of hilar cholangiocarcinoma[J].Chinese Clinical Oncology, 2015,20(8):760-764.
[14] 于同波, 刘程, 周珍娟, 等.血清CEA、CA125、CA199及血浆M2-PK联合检测胃癌的诊断价值研究[J].中国实用医药, 2018,13(24):3-5.doi:10.14163/j.cnki.11-5547/r.2018.24.002.Yu TB, Liu C, Zhou ZJ, e al.Diagnostic value research of combined detection of serum CEA, CA125, CA199 and plasma M2-PK in gastric cancer[J].China Practical Medical, 2018, 13(24):3-5.doi:10.14163/j.cnki.11-5547/r.2018.24.002.
[15] 陈光侠, 何晓华, 吴倩倩, 等.丙酮酸激酶M2蛋白表达与各期胃癌临床病理特征及预后的相关性分析[J].临床外科杂志, 2017,25(11):859-862.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1005-6483.2017.11.019.Chen GX, He XH, Wu QQ, et al.A correlation analysis of the expression of pyruvate kinase M2 and the pathology and prognosis in gastric cancer[J].Journal of Clinical Surgery, 2017, 25(11):859-862.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1005-6483.2017.11.019.
[16] 钟世洪, 成志烜, 王卓.血清CEA、CA199、CA125及血浆M2-PK联合检测在胃癌诊断中的临床研究[J].基层医学论坛, 2018,22(1):1-2.doi:10.19435/j.1672-1721.2018.01.001.Zhong SH, Cheng ZH, Wang Z.Clinical study on joint detection of serum CEA, CA199, CA125 and plasma M2-PK in the diagnosis of gastric cancer[J].The Medical Forum, 2018, 22(1):1-2.doi:10.19435/j.1672-1721.2018.01.001.
[17] 李静, 黄亮, 周飞国, 等.肿瘤型丙酮酸激酶M2在胰腺癌中的表达特点及其临床病理联系[J].中华临床医师杂志:电子版, 2011,5(19):5630-5634.doi:10.3877/cma.j.issn.1674-0785.2011.19.018.Li J, Huang L, Zhou FG, et al.Expression of tumour pyruvate kinase type M2 on pancreatic cancer and it′s clinicopathologic connection[J].Chinese Journal of Clinicians:Electronic Edition, 2011, 5(19):5630-5634.doi:10.3877/cma.j.issn.1674-0785.2011.19.018.
[18] 王琼, 吕秋琼, 尉理梁.血浆M2-PK与血清CEA、ADAM8联合检测诊断非小细胞肺癌的临床价值研究[J].医学研究杂志, 2017,46(10):187-189.doi:10.11969/j.issn.1673-548X.2017.10.046.Wang Q, Lu QQ, Wei LL.Value of Combined Determination of Plasma M2-PK, Serum CEA and ADAM8 in the Diagnosis of Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer[J].Journal of Medical Research, 2017,46(10):187-189.doi:10.11969/j.issn.1673-548X.2017.10.046.
[19] 陈树林, 张妮, 肖倩, 等.血清ADAM8、CEA与血浆M2-PK三者单独及联合检测在非小细胞肺癌早期诊断中的价值[J].标记免疫分析与临床, 2016, 23(3):248-251.doi:10.11748/bjmy.issn.1006-1703.2016.03.004.Chen SL, Zhang N, Xiao Q, et al.Value of Combined Detection of ADAM8, CEA and M2-PK in Diagnosis of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer in the Early Stage[J].Labeled Immunoassays and Clinical Medicine, 2016, 23(3):248-251.doi:10.11748/bjmy.issn.1006-1703.2016.03.004.
[20] 刘玉兰, 何凤屏, 徐新, 等.实时荧光定量PCR检测结直肠癌患者粪便肿瘤型M2-PK DNA及临床应用研究[J].国际检验医学杂志, 2017, 38(11):1444-1446.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-4130.2017.11.002.Liu YL, He FP, Xu X, et al.Clinical application of real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR for the detection of fecal tumor M2-pyruvate kinase in colorectal cancer patients[J].International Journal of Laboratory Medicine, 2017, 38(11):1444-1446.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-4130.2017.11.002.
[21] 管振祺, 何凤屏, 徐新, 等.肿瘤型M 2-PK、APC、K-ras检测在结直肠癌诊断中的意义[J].国际检验医学杂志, 2017, 38(5):582-584.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-4130.2017.05.003.Guan ZQ, He FP, Xu X, et al.Clinical significance of combined detection of fecal tumor M2-PK ,APC ,K-ras expression in early diagnosing colorectal cancer[J].International Journal of Laboratory Medicine, 2017, 38(5):582-584.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-4130.2017.05.003.
[22] 柴浩, 熊新魁, 孙道一, 等.PKM2基因对胆管细胞癌迁移、侵袭及增殖的影响[J].南京医科大学学报:自然科学版, 2015,35(5):615-621.doi: 10.7655/NYDXBNS20150504.Chai H, Xiong XK, Sun DY, et al.Au experimental research on PKM2 gene on migration, invasion and proliferation of cholangiocarcinoma cell line[J].Acta Universitatis Medicinalis Nanjing, 2015, 35(5):615-621.doi: 10.7655/NYDXBNS20150504.
[23] 林德照, 蔡文品, 陈跃.血清肿瘤型M2丙酮酸激酶在直肠癌早期诊断中的应用价值[J].中国卫生检验杂志, 2016, 26(13):1877-1879.Lin DZ, Cai WP, Chen Y.Value of serum tumor M2 pyruvate kinase in the early diagnosis of rectal cancer Chinese[J].Journal of Health Laboratory Technology, 2016, 26(13):1877-1879.
[24] 杨春云.血浆肿瘤型M2丙酮酸激酶在直肠癌诊断与病情监测中的价值[J].国际检验医学杂志, 2016, 37(12):1654-1656.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-4130.2016.12.022.Yang CY.Value of plasma tumor M2 pyruvate kinase in diagnosis and monitoring of rectal cancer[J].International Journal of Laboratory Medicine, 2016, 37(12):1654-1656.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-4130.2016.12.022.
[25] 吴刚, 闫文锋, 张建成, 等.胃癌患者血清肿瘤型M2丙酮酸激酶水平变化及意义[J].医药论坛杂志, 2015, 36(8):14-15.Wu G, Yan WF, Zhang JC, et al.Changes and significance of serum tumor type M2 pyruvate kinase in patients with gastric cancer[J].Journal of Medical Forum, 2015, 36(8):14-15.
[26] Liu WR, Tian MX, Yang LX, et al.PKM2 promotes metastasis by recruiting myeloid-derived suppressor cells and indicates poor prognosis for hepatocellular carcinoma[J].Oncotarget, 2015 ,6(2):846-861.doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2749.
[27] Wang LY, Liu YP, Chen LG, et al.Pyruvate kinase M2 plays a dual role on regulation of the EGF/EGFR signaling via E-cadherindependent manner in gastric cancer cells [J].PLoS One, 2013,8(6):e67542.doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0067542.
[28] Feng J, Ma T, Ge Z, et al.PKM2 gene regulates the behavior of pancreatic cancer cells via mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways[J].Mol Med Rep, 2015, 11(3):2111-2117.doi: 10.3892/mmr.2014.2990.
[29] Zhou CF, Li XB, Sun H, et al.Pyruvate kinase type M2 is upregulated in colorectal cancer and promotes proliferation and migration of colon cancer cells[J].IUBMB Life, 2012, 64(9):775-782.doi: 10.1002/iub.1066.
[30] Li YG, Zhang N.Clinical significance of serum tumour M2-PK and CA19-9 detection in the diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma [J].Dig Liver Dis, 2009, 41(8):605-608.doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2008.11.010.
[31] 张雁鹏, 王世明, 韩栓柱.肿瘤标志物联合检测在肝门胆管癌诊断和治疗中的研究进展[J].中国现代医生, 2017, 55(1):162-165.Zhang YP, Wang SM, Han SZ.Research advances of combined detection of tumor markers in the diagnosis and treatment of hilar cholangiocarcinoma[J].China Modern Doctor, 2017, 55(1):162-165.
[32] 周娥.血清CEA 、CA125、CA199及血浆M2-PK联合检测在胃癌诊断中的价值分析[J].检验医学与临床, 2016, 13(16):2360-2362.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-9455.2016.16.051.Zhou E.Analysis of the value of combined examination of serum CEA, CA125, CA199 and plasma M2-PK in diagnosis of gastric cancer[J].Laboratory Medicine and Clinic, 2016, 13(16):2360-2362.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-9455.2016.16.051.
[33] 杨刚, 唐丽娟.血清 T uM 2-PK 、CEA 、CA19-9和CA72-4对结肠癌的筛查价值[J].检验医学与临床, 2017, 14(1):35-36.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-9455.2017.01.012.Yang G, Tang LJ.Screening value of serum M2-PK,CEA,CA19-9 and CA72-4 for colon cancer[J].Laboratory Medicine and Clinic,2017, 14(1):35-36.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-9455.2017.01.012.
[34] Wang B, Chen L, Chang HT.Potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for cholangiocarcinoma in serum and bile[J].Biomark Med, 2016, 10(6):613-619.doi: 10.2217/bmm-2015-0062.
[35] 李明岳, 鲍世韵, 刘嘉林, 等.组蛋白H3K9me3在胆管癌发生机制中的作用[J].中华实验外科杂志, 2015, 32(6):1404-1409.doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-9030.2015.06.069.Li MY, Bao SY, Liu JL, et al.The role of histone H3 lysine 9 trimethylation modification on cholangiocarcinoma moleculor mechanism[J].Chinese Journal of Experimental Surgery, 2015,32(6):1404-1409.doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-9030.2015.06.069.
[36] 舍玲.胃癌BGC-823细胞中HIF-1α、HIF-2α对GLUT1、PKM2的调控作用[D].乌鲁木齐: 新疆医科大学, 2017.She L.Regulatory effects of HIF-1α and HIF-2α on GLUT1 and PKM2 in gastric cancer BGC-823 cells[D].Urumchi: Xinjiang Medical University, 2017.
[37] 李志艳.二烯丙基二硫抑制PKM2干扰胃癌细胞能量代谢[D].衡阳: 南华大学, 2017.Li ZY.Diallyl disulfide suppresses aerobic glycolysis by downregul ating PKM2 in gastric cancer cells[D].Hengyang: University Of South China, 2017.
[38] 唐然.miR-let-7a通过降低PKM2表达抑制胃癌细胞增殖、迁徙和转移[D].南京: 南京医科大学, 2016.Tang R.MiR-let-7a inhibiting the proliferation, migration and metastasis of gastric cancer cells through decreasing PKM2 expression[D].Nanjing: Nanjing Medical University, 2016.
