近年来,随着血管腔内外科的迅猛发展,腹主动脉瘤腔内修复术(endovascular aneurysm repair,EVAR)已逐渐成为治疗腹主动脉瘤(abdominal aortic aneurysm,AAA)的首选方法。虽然EVAR的远期生存率与开放手术相比无显著差异,但是其围手术期的不良事件发生率较低[1],有研究[2-3]表明,开放手术的30d病死率大约为EVAR 的3~4倍。随着腔内技术和器械的不断发展,EVAR的平均手术时长、平均住院日以及围手术期并发症率近年来均下降明显[3-4]。然而,符合传统EVAR解剖标准的AAA患者仅占所有AAA患者总数的50%左右[5],病变血管解剖结构的复杂性仍是制约腔内技术发展的主要因素。本文拟结合不同腔内技术,对复杂腹主动脉瘤对近端锚定区的要求及相关临床证据进行简要讨论。
近端锚定区的解剖形态与I 型内漏、支架移位、术后二次干预率密切相关[6]。因此,正确评估近端锚定区,选择合理的腔内治疗方案,是AAA疾病治疗的关键。不同支架对近端锚定区的要求不尽相同(表1)[7]。一般而言,传统EVAR对近端锚定区的要求需符合:(1)近端瘤颈长度≥15 mm;(2)近端瘤颈与腹主动脉主干轴成角≤60°;(3)近端瘤颈直径≤30 mm;(4)锚定区形态规则,无严重钙化及附壁血栓[8]。随着手术器械和技术的不断改进,部分超适应证的病例不再是EVAR的绝对禁忌。对于某些近端锚定区不良的复杂腹主动脉瘤,采用不同的治疗策略,也可以获得相对满意的临床效果。近年来,包括“烟囱支架”、“开窗型支架”以及“分支型支架”等器械用于临床的报道已不少见,为处理合并不良近端锚定区的AAA带来了更多的选择。
表1 不同支架对近端锚定区的要求
Table 1 Proximal landing zone requirements of different stents
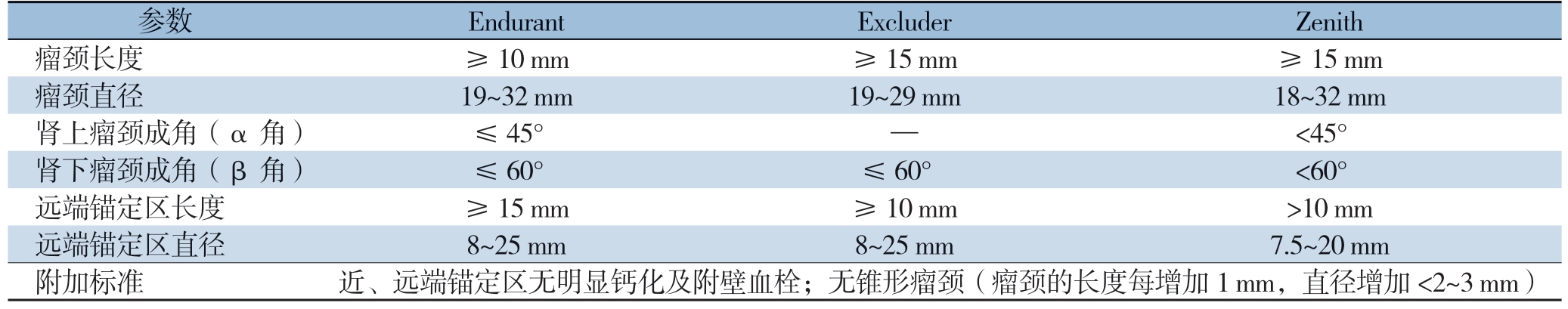
参数 Endurant Excluder Zenith瘤颈长度 ≥10 mm ≥15 mm ≥15 mm瘤颈直径 19~32 mm 19~29 mm 18~32 mm肾上瘤颈成角(α 角)≤45° — <45°肾下瘤颈成角(β 角)≤60° ≤60° <60°远端锚定区长度 ≥15 mm ≥10 mm >10 mm远端锚定区直径 8~25 mm 8~25 mm 7.5~20 mm附加标准 近、远端锚定区无明显钙化及附壁血栓;无锥形瘤颈(瘤颈的长度每增加1 mm,直径增加<2~3 mm)
1 烟囱技术
“烟囱技术”是指当植入主动脉支架主体时,由于近端锚定区长度不足,在锚定区应用裸支架或覆膜支架与主体支架并行释放,进而达到保留被覆盖分支血管的目的。该技术最初被应用于错误覆盖弓上分支动脉的挽救性手术中,后来逐渐在近肾型腹主动脉瘤的腔内修复术中得到推广。有研究[7,9]提示,烟囱技术在近端锚定区≥15 mm、烟囱支架数量≤2个、近端锚定区主体支架的扩张率为30%时可以获得相对良好的手术效果。烟囱技术操作简单,对近端锚定区及器材的要求较低,当瘤颈长度在10~15 mm时,可以从一定程度上将近端锚定区延长3~5 mm。但是,由于烟囱支架与主体支架的近端开口并行,增加了I 型内漏可能性。随着烟囱支架植入数量的增加,内漏的风险也更高。目前,应用烟囱技术治疗复杂腹主动脉瘤的病例报道并不少见,但是多中心、大规模、长期的临床研究较少。PERICLES临床注册研究是迄今为止最大的应用烟囱技术治疗复杂腹主动脉瘤的临床研究[10],纳入了2008—2014年欧美多中心采用烟囱技术治疗腹主动脉瘤的517例患者,共植入898枚烟囱支架(球扩式支架49.2%,自膨式支架39.6%,金属裸支架11.2%),技术成功率为97.1%,30 d病死率为3.7%,中位随访时间17.1个月,烟囱支架的通畅率为94%,内漏发生率为2.9%。我中心曾经统计了2005—2013年全球范围内采用开窗及烟囱技术治疗近肾型腹主动脉瘤患者共700例(烟囱支架158例,开窗支架542例)[11],其中,接受烟囱技术的患者30 d病死率为3.8%,中位随访14个月,I 型、II型和III型内漏的发生率分别为11.8%、8.1%和0.4%。尽管烟囱技术对近端锚定区和器材的要求不高,但是基于其原理上的缺陷,在使用时仍建议作为次要选择,通常在急诊手术或是开窗和分支支架无法实施的高风险患者中实施。
2 开窗技术
“开窗型支架”设计之初是为了治疗无法应用常规器材处理的肾周型AAA。开窗技术最早应用于1999年[12],能够实现完全腔内重建肾动脉及内脏分支动脉的目的,是EVAR发展过程中的一次重大革新。商业化的开窗型支架以COOK公司的ZENITH定制型支架系统为代表。近年来,很多中心也基于常规的器材和患者的病变血管解剖形态,对器材进行加工改良,采用“预开窗”或者是“原位开窗”的方式来重建肾动脉及内脏分支动脉。其优点是无需定制器械,但是临床效果往往取决于手术医生的个人经验和操作技巧,难以大规模推广。开窗型支架从某种程度上可以解决“短瘤颈”或者是锚定区不足的难题,但是仍应严格掌握相应的近端锚定区解剖条件。从我中心的经验来看[8],近端瘤颈长度应在4~15 mm,直径19~30 mm,与主动脉瘤长轴的成角应≤45°,锚定区需确保无严重的钙化、溃疡和附壁血栓。虽然开窗型支架对患者的解剖要求较高,操作难度大,但仍可以作为腔内治疗近端锚定区不良腹主动脉瘤的首选方式[13]。过去已有的文献[14]提示:开窗型支架治疗腹主动脉瘤的总体技术成功率在90%~100%,30 d病死率为3.3%,术后肾损伤率为16.2%,二次干预率为6.1%,内漏率为4.9%,靶血管通畅率为96%。另一项前瞻性的多中心临床注册研究[15]显示,开窗技术的手术成功率为99%,30 d病死率4.1%,术后1、2、3年的二次干预率分别为10%,14%和30%,靶血管通畅率分别为93%、91%和89%。值得注意的是,当采用开窗型支架治疗复杂腹主动脉瘤时,应适当控制“窗口”的数量。Patel等[16]研究发现,采用两开窗的AAA患者其30 d病死率为2%,而采用四开窗支架的AAA患者其30 d病死率高达24%。WINDOWS临床注册研究中的结果也显示,近肾型腹主动脉瘤患者的围手术期病死率为6.5%,而肾上型和胸腹主动脉瘤患者的围手术期病死率为14.3%[17],表明开窗型支架在腔内治疗肾上型腹主动脉瘤、胸腹主动脉瘤时仍是谨慎选择。
3 分支型支架
对于肾上型腹主动脉瘤以及胸腹主动脉瘤而言,“多分支支架”是一种可行的选择。多分支支架的原理是在主动脉主体支架上延伸出不同数目的分支,植入时将多个分支分别与靶血管的桥接支架进行连接,从而实现重建多内脏分支动脉的目的。COOK公司的T-branch是目前唯一的可用于直接治疗复杂主动脉瘤的商业化多分支支架[18-19]。根据Bosiers等[20]的报道,为了尽可能达到良好的临床效果,符合T-branch解剖结构的患者需满足:(1)瘤颈的最大直径<38 mm;(2)锚定区长度≥20 mm;(3)内脏区域主动脉直径≥25 mm;(4)靶血管数≤4;(5)靶血管直径>4 mm。T-branch在全球范围内的植入数量已逾千例,其总体技术成功率为87%~97%,30 d病死率4%~9%,术后脊髓缺血的发生率3%~16.7%,二次干预率88%[21-22]。目前,T-branch在我国仍未获得上市许可,但是新型国产多分支支架已进入临床试验阶段。相信在不远的将来,随着不同多分支支架应用于临床,越来越多近端锚定区不良的腹主、胸腹主动脉瘤都可以采用完全腔内的方法进行治疗。
4 小 结
随着新技术、新器械的不断迭代更新,不良的近端锚定区在很大程度上已不再是复杂腹主动脉瘤腔内修复术的禁忌。诸多的临床证据已经证实了腔内修复术在复杂腹主动脉瘤治疗的重要作用。未来,新的适应性更广的器材将造福更多的患者,也将促进血管腔内外科的不断发展。
[1]Lederle FA,Freischlag JA,Kyriakides TC,et al.Outcomes following endovascular vs open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm:a randomized trial[J].JAMA,2009,302(14):1535-1542.doi:10.1001/jama.2009.1426.
[2]Budtz-Lilly J,Venermo M,Debus S,et al.Editor's Choice-Assessment of International Outcomes of Intact Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair over 9 Years[J].Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg,2017,54(1):13-20.doi:10.1016/j.ejvs.2017.03.003.
[3]Yin K,Locham SS,Schermerhorn ML,et al.Trends of 30-day mortality and morbidities in endovascular repair of intact abdominal aortic aneurysm during the last decade[J].J Vasc Surg,2019,69(1):64-73.doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2018.04.032.
[4]Gavali H,Mani K,Tegler G et al.Editor's Choice-Prolonged ICU Length of Stay after AAA Repair:Analysis of Time Trends and Long-term Outcome[J].Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg,2017,54(2):157-163.doi:10.1016/j.ejvs.2017.05.014.
[5]Elkouri S,Martelli E,Gloviczki P,et al.Most patients with abdominal aortic aneurysm are not suitable for endovascular repair using currently approved bifurcated stent-grafts[J].Vasc Endovascular Surg,2004,38(5):401-412.doi:10.1177/153857440403800502.
[6]Marone EM,Freyrie A,Ruotolo C,et al.Expert Opinion on Hostile Neck Definition in Endovascular Treatment of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms(a Delphi Consensus)[J].Ann Vasc Surg,2020,62:173-182.doi:10.1016/j.avsg.2019.05.049.
[7]Wanhainen A,Verzini F,Van Herzeele I,et al.Editor's Choice-European Society for Vascular Surgery(ESVS)2019 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the Management of Abdominal Aorto-iliac Artery Aneurysms[J].Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg,2019,57(1):8-93.doi:10.1016/j.ejvs.2018.09.020.
[8]张韬,贾鑫,刘杰,等.近端锚定区不良的腹主动脉瘤腔内治疗方案选择及疗效评价[J].中华医学杂志,2012,92(47):3329-3332.doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2012.47.006.
Zhang T,Jia X,Liu J,et al.Approach and effi cacy of endovascular repair for abdominal aortic aneurysm with hostile proximal landing zone[J].National Medical Journal of China,2012,92(47):3329-3332.doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2012.47.006.
[9]Mestres G,Yugueros X,Apodaka A,et al.The best in vitro conditions for two and three parallel stenting during endovascular aneurysm repair[J].J Vasc Surg,2017,66(4):1227-1235.doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2016.09.046.
[10]Donas KP,Lee JT,Lachat M,et al.Collected world experience about the performance of the snorkel/chimney endovascular technique in the treatment of complex aortic pathologies:the PERICLES registry[J].Ann Surg,2015,262(3):546-553.doi:10.1097/SLA.0000000000001405.
[11]Li Y,Hu Z,Bai C,et al.Fenestrated and Chimney Technique for Juxtarenal Aortic Aneurysm:A Systematic Review and Pooled Data Analysis[J].Sci Rep,2016,6:20497.doi:10.1038/srep20497.
[12]Browne TF,Hartley D,Purchas S,et al.A fenestrated covered suprarenal aortic stent[J].Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg,1999,18(5):445-449.doi:10.1053/ejvs.1999.0924.
[13]Verhoeven EL,Katsargyris A,Oikonomou K,et al.Fenestrated Endovascular Aortic Aneurysm Repair as a First Line Treatment Option to Treat Short Necked,Juxtarenal,and Suprarenal Aneurysms[J].Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg,2016,51(6):775-781.doi:10.1016/j.ejvs.2015.12.014.
[14]Jones AD,Waduud MA,Walker P,et al.Meta-analysis of fenestrated endovascular aneurysm repair versus open surgical repair of juxtarenal abdominal aortic aneurysms over the last 10 years[J].BJS Open,2019,3(5):572-584.doi:10.1002/bjs5.50178.
[15]British Society for Endovascular Therapy and the Global Collaborators on Advanced Stent-Graft Techniques for Aneurysm Repair(GLOBALSTAR)Registry.Early Results of Fenestrated Endovascular Repair of Juxtarenal Aortic Aneurysms in the United Kingdom[J].Circulation,2012,125(22):2707-2715.doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.070334.
[16]Patel SD,Constantinou J,Simring D,et al.Results of complex aortic stent grafting of abdominal aortic aneurysms stratified according to the proximal landing zone using the Society for Vascular Surgery classification[J].J Vasc Surg,2015,62(2):319-325.doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2015.03.035.
[17]Marzelle J,Presles E,Becquemin JP,et al.Results and Factors Affecting Early Outcome of Fenestrated and/or Branched Stent Grafts for Aortic Aneurysms:A Multicenter Prospective Study[J].Ann Surg,2015,261(1):197-206.doi:10.1097/SLA.0000000000000612.
[18]Gallitto E,Gargiulo M,Freyrie A,et al.Off-the-shelf multibranched endograft for urgent endovascular repair of thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms[J].J Vasc Surg,2017,66(3):696-704.doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2016.12.129.
[19]Mendes BC,Oderich GS.Endovascular repair of thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm using the off-the-shelf multibranched t-Branch stent graft[J].J Vasc Surg,2016,63(5):1394-1399.doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2016.02.021.
[20]Bosiers MJ,Bisdas T,Donas KP,et al.Early experience with the first commercially available off-the-shelf multibranched endograft(t-branch)in the treatment of thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms[J].J Endovasc Ther,2013,20(6):719-725.doi:10.1583/13-4428R.1.
[21]Verhoeven EL,Katsargyris A,Bekkema F,et al.Editor's Choice-Ten-year Experience with Endovascular Repair of Thoracoabdominal Aortic Aneurysms:Results from 166 Consecutive Patients[J].Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg,2015,49(5):524-531.doi:10.1016/j.ejvs.2014.11.018.
[22]Guillou M,Bianchini A,Sobocinski J,et al.Endovascular treatment of thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms[J].J Vasc Surg,2012,56(1):65-73.doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2012.01.008.

