- Chinese expert consensus on robotic-assisted hiatal hernia repair with anti-reflux surgery in adults (2024 Edition)
- Laparoscopic standardized seven-step surgical operative guidelines for hiatal hernia and gastroesophageal reflux disease (2025 edition)
- Application of the "necktie technique" in laparoscopic esophageal hiatal hernia repair and fundoplication surgery
- Interpretation of the Japanese Clinical practice guidelines for the management of retroperitoneal sarcoma and clinical advances
- Causes and prevention strategies of surgical complications in laparoscopic hiatal hernia repair with mesh and fundoplication: a single-center analysis of 432 cases
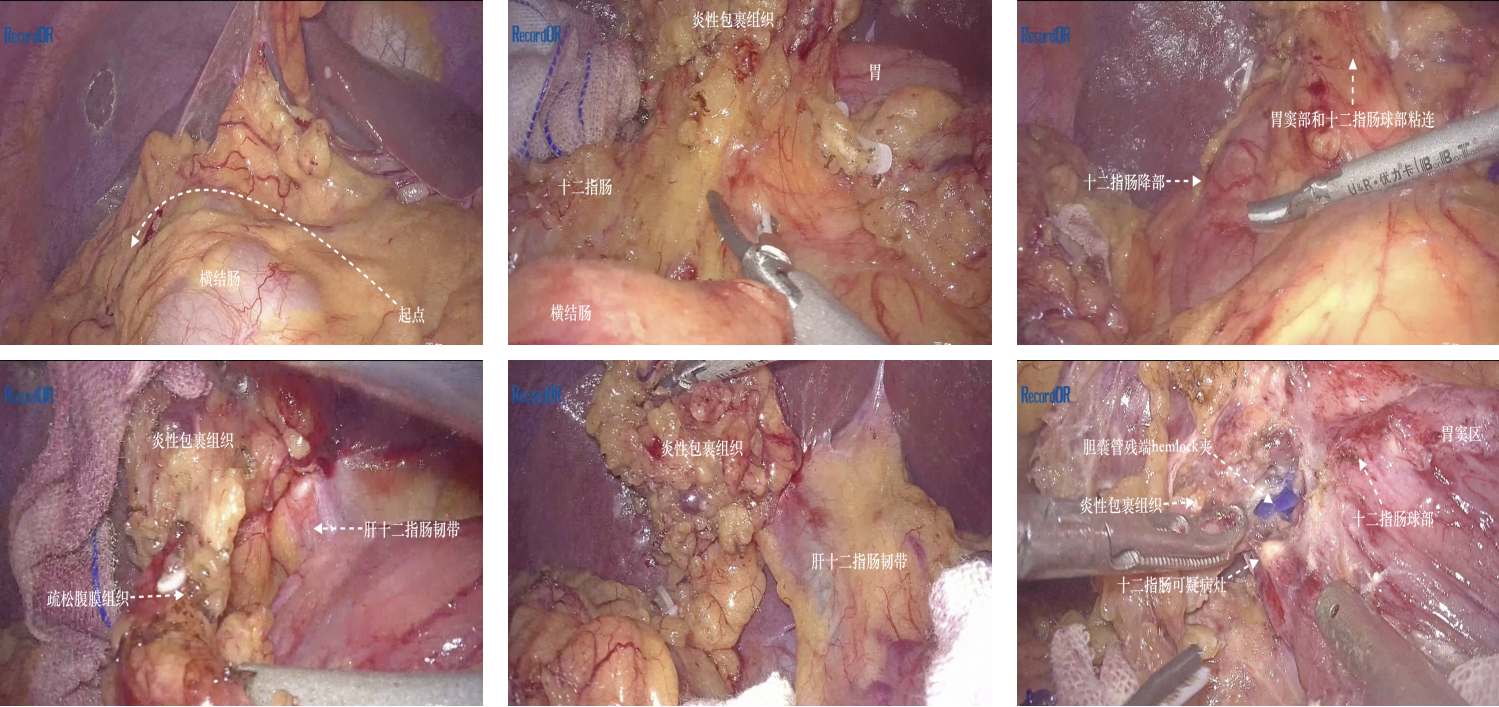
- In situ laparoscopic pancreaticoduodenectomy via the left-sided combined middle approach: a report of 4 cases
- Cross-sectional analysis and prospective prediction of pancreatic cancer disease burden based on the GBD database
- Clinical study of a novel transabdominal approach guiding sphincterotomy for choledocholithiasis complicated by stenosis of the ampulla of Vater
- The challenges and strategies of conversion therapy for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma with middle hepatic vein invasion
- Application strategy of programmatic improvement in laparoscopic transcystic common bile duct exploration·
- Progress and considerations in delayed radical surgery for incidental gallbladder cancer: clinical application of 3D laparoscopic PH approach
- Understanding and reflection on the standardized treatment of hepatolithiasis
- Hunan expert consensus on comprehensive diagnosis and treatment of hilar cholangiocarcinoma (2025 edition)
- Relationship between PD-L1 expression and the STAT3/PRKDC/MYC signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Development and key points of laparoscopic portal territory anatomical liver resection
- Safety and efficacy of robotic-assisted vs. laparoscopic hepatectomy for the treatment of hepatic hemangiomas
- Current Issue
- Published Ahead-of-Print
- Virtual Issues
- Previous Issues
-
2025,34(4):595-599, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250210
Abstract:
The surgical approach for hiatal hernia repair with anti-reflux procedures has transitioned from traditional open thoracotomy to the era of minimally invasive techniques. In recent years, laparoscopic surgery has been widely applied in hiatal hernia repair. Robotic-assisted hiatal hernia repair represents an important trend in the development of minimally invasive surgery for this condition and has seen rapid progress in recent years. However, there is currently no definitive guideline for clinical practice. To further standardize the robotic surgical treatment of hiatal hernia, the Expert Working Group of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease of Surgeons Society of Chinese Medical Doctor Association, building upon the 2023 consensus, took the lead in organizing domestic experts in related fields to review relevant literature from both China and abroad, discuss key issues and challenges, and formulate the 2024 edition of the expert consensus. This resulted in the publication of the “Chinese expert consensus on robotic-assisted hiatal hernia repair with anti-reflux surgery in adults (2024 Edition)”, which aims to provide guidance and reference for the continued advancement of robotic hiatal hernia surgery in China.
-
2025,34(4):600-613, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250074
Abstract:
Based on the "Laparoscopic standardized seven-step surgical procedure guidelines for hiatal hernia and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) (2021 edition)", this guideline updates the evidence-based evidence from the past four years. It aims to provide standardized and homogenized guidance for the surgical treatment of GERD and hiatal hernia. The guideline elaborates on preoperative examination, surgical indications, contraindications, preoperative preparation, surgical steps, postoperative management, and follow-up. The surgical procedure follows a seven-step approach, which includes placement of trocars, abdominal cavity exploration, mobilization of the abdominal esophagus, closure of the hiatal defect, reinforcement of the diaphragmatic crura with mesh fixation, construction of the anti-reflux valve mechanism, irrigation of the operative field and closure of port sites. The guideline emphasizes the importance of preoperative multidisciplinary evaluation, individualized surgical planning, and management of postoperative complications, aiming to enhance the safety and effectiveness of surgery, reduce postoperative complications, and improve the patient's quality of life.
-
ZHANG Yiqiao, LIU Yang, ZHANG Zhongtao
2025,34(4):614-624, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250099
Abstract:
Obesity, as a major global public health issue, has seen effective improvements in body weight and metabolic disorders through bariatric-metabolic surgeries such as Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) and sleeve gastrectomy (SG). However, the management of postoperative complications remains a significant clinical challenge. Gastrointestinal leakage/fistula is one of the more severe complications, and current endoscopic treatment options include stent placement, double-pigtail stent internal drainage, over-the-scope clips, endoscopic suturing, tissue adhesive sealing, negative pressure drainage systems, and gastric wall incision. The combination with laparoscopic techniques can further enhance treatment efficacy. For SG-related torsion or stenosis, endoscopic balloon dilation is the first-line approach. In refractory cases, additional therapies such as endoscopic radial incision or modified gastric peroral endoscopic myotomy (G-POEM) may be required. G-POEM offers particular advantages in treating non-spiral stenosis but remains limited in practice due to technical complexity. Postoperative gastrointestinal bleeding requires stratified management: thermal coagulation or hemostatic clips can be used in acute bleeding; marginal ulcer bleeding at the gastrojejunostomy site after RYGB responds well to endoscopic treatment, while bleeding at the jejunojejunostomy site often requires enteroscopy or reoperation. Anatomical changes after RYGB increase the complexity of managing common bile duct stones. Among improved endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) techniques, endoscopic ultrasound-guided transgastric ERCP has emerged as a minimally invasive and efficient option, though its long-term safety remains to be fully validated. For patients experiencing weight regain, endoscopic interventions include endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty and transoral outlet reduction (TORe), with TORe offering the dual benefits of narrowing the anastomosis and relieving dumping syndrome. The risk of gastroesophageal reflux disease increases after SG; balloon dilation can relieve reflux caused by anatomical stenosis, while emerging techniques such as anti-reflux mucosal resection and anti-reflux mucosal ablation are still under exploration. In refractory GERD cases, conversion to RYGB remains the mainstream solution. Overall, endoscopic techniques have significantly reduced reoperation rates through diverse strategies, but a balance must be maintained between procedural complexity and long-term efficacy. Future efforts should focus on device innovation, standardization of procedures, and multidisciplinary collaboration to improve the comprehensive management of complications following bariatric-metabolic surgery.
-
LI Baopeng, GAO Xiang, LI Pengzhou, ZHU Liyong, ZHU Shaihong
2025,34(4):625-631, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250100
Abstract:
Obesity has become a global public health crisis, attracting significant attention due to its association with metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, and various cancers. Bariatric-metabolic surgery, as a long-term effective method for weight management, can significantly reduce visceral and subcutaneous fat, improving metabolic health. However, it is also crucial to recognize the postoperative decline in muscle mass and bone density, which can lead to a series of related issues, adversely affecting patients' physical health and quality of life. Given this complex clinical reality, research on postoperative body composition changes becomes particularly important. Here, the authors systematically summarize the characteristics of body composition changes at different stages after bariatric-metabolic surgery, delves into the clinical significance of body composition loss, and provides a forward-looking perspective on the future development of this field, aiming to develop more scientific and reasonable postoperative management strategies for clinical practice.
-
XU Jinghao, LIU Danlu, DU Qiang, WAN Qianyi, ZHAO Rui, ZHANG Guixiang, CHENG Zhong, CHEN Yi
2025,34(4):632-639, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250098
Abstract:
Metabolic-bariatric surgery (MBS) has become an important treatment for pathological obesity and metabolic diseases. However, common postoperative nutritional complications—such as protein-energy malnutrition, iron deficiency anemia, and vitamin B12 deficiency—significantly affect patients' long-term prognosis. Traditional nutritional management models rely on static monitoring and standardized supplementation, which are insufficient to address individual variability and dynamic postoperative changes. Artificial intelligence (AI), through integrating multimodal data (such as biochemical indicators, imaging information, and wearable device monitoring) and intelligent modeling, offers new approaches for dynamic monitoring, risk prediction, and personalized intervention. Based on literature from 2017 to 2025, this article systematically evaluates the application of AI in perioperative nutritional management for MBS, covering key technologies including machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing. It also analyzes current challenges in clinical translation, such as data fragmentation, lack of model interpretability, and limited long-term validation. In the future, enhanced multi-center collaboration, the development of standardized databases, and explainable models will be essential to advancing nutritional management in MBS from empirical practice to precision medicine.
-
XUE Peng, MA Ning, ZHOU Taicheng
2025,34(4):640-647, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250111
Abstract:
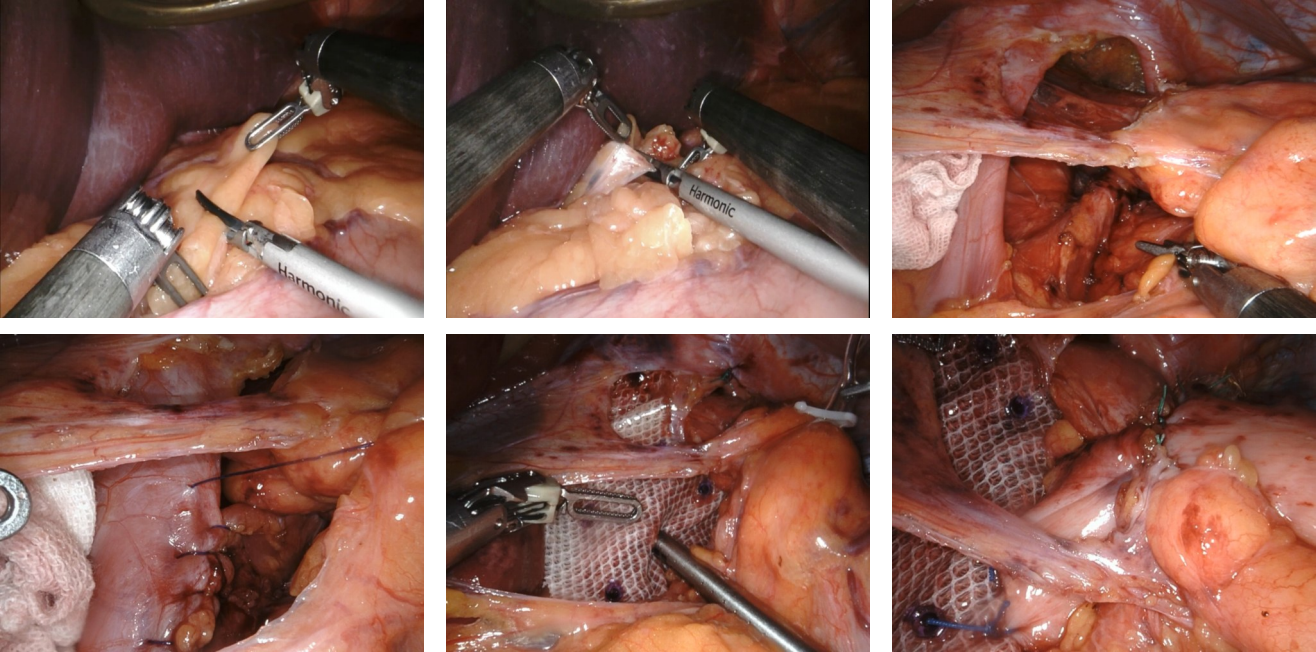
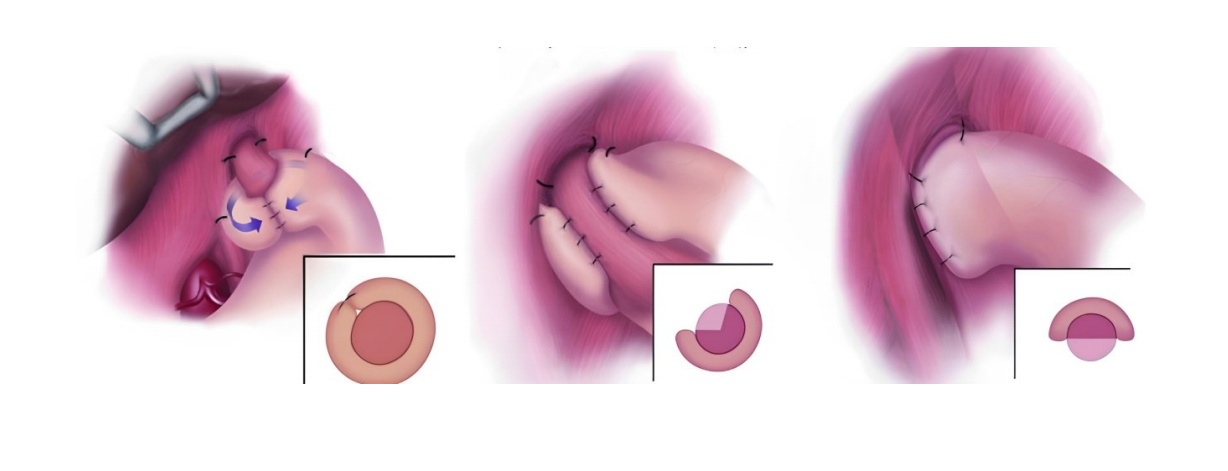
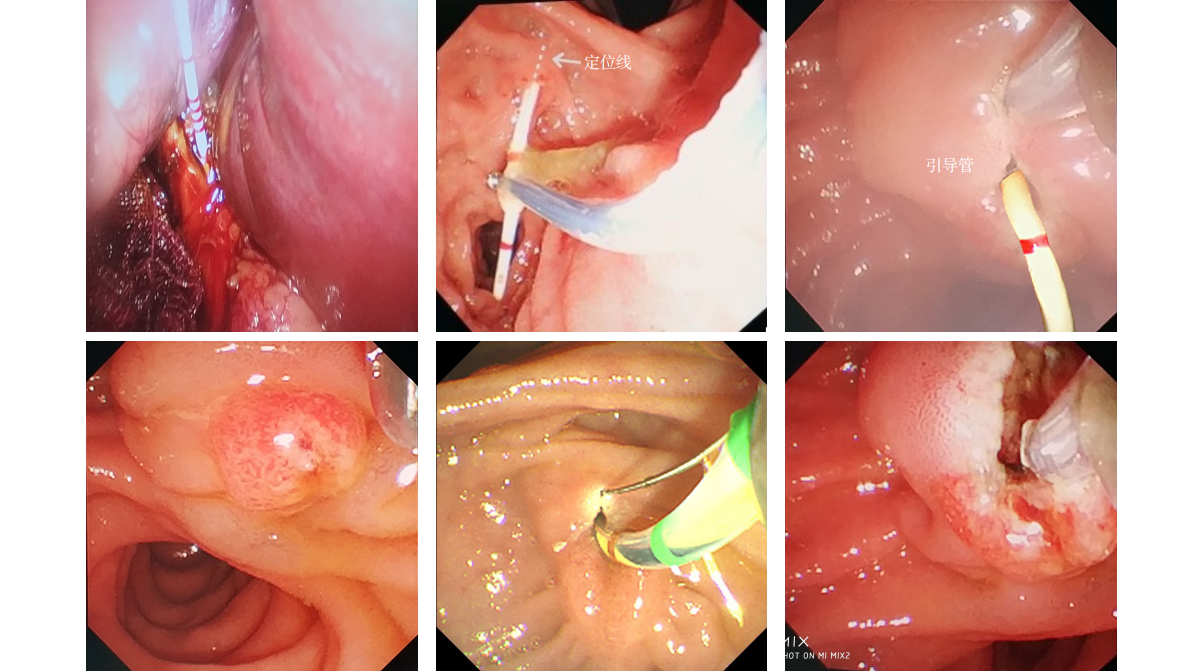
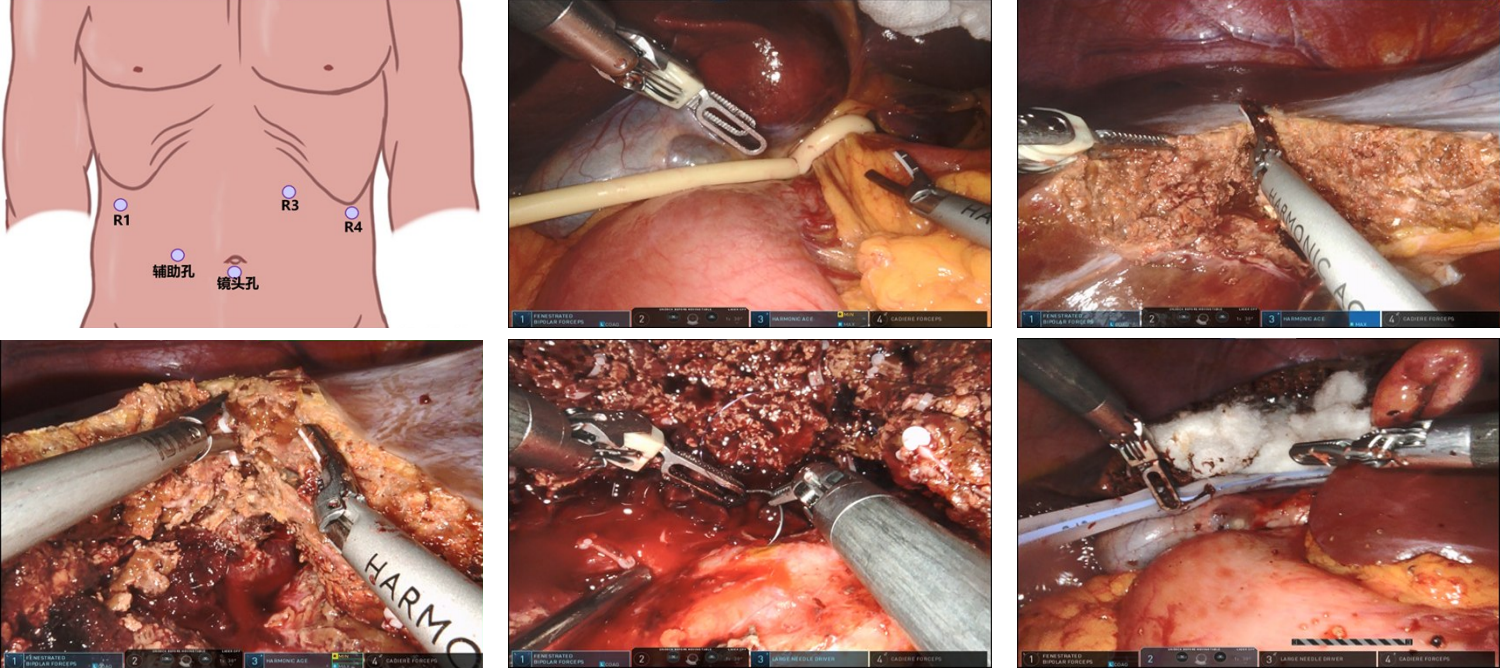
With the rising incidence of hiatal hernia and gastroesophageal reflux disease, surgical techniques urgently require refinement to improve patient outcomes. Guided by the concept of "anatomical priority", Professor Chen Shuang's team has established a standardized seven-step laparoscopic protocol, emphasizing three key components: precise dissection of the "sacred plane", three-dimensional crural reconstruction, and tension-controlled fundoplication. To address limitations such as restricted intraoperative visualization and poor reproducibility, the team further developed the innovative "necktie traction technique". This method employs a red pediatric catheter to create a dynamic traction system, enabling directional field exposure, axial esophageal repositioning, and quantitative control of fundoplication. Integrating biomechanical principles, the technique provides a visualized and standardized operative pathway, significantly enhancing surgical safety, efficacy, and reproducibility. As a novel approach combining anatomical restoration with functional anti-reflux reconstruction, the "necktie technique" offers robust technical support for the standardized promotion of laparoscopic anti-reflux surgery.
-
SUN Zhipeng, SONG Haoyu, LI Wengang
2025,34(4):648-659, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250147
Abstract:
Retroperitoneal sarcoma is a rare but highly malignant type of soft tissue tumor, and its diagnosis and treatment have long been focal points in clinical research. In December 2021, the Japanese Society for Sarcoma Research, together with several other medical organizations, published the Clinical practice guidelines for the management of retroperitoneal sarcoma, which were revised in April 2023. The guidelines provide recommendations on three key aspects: the diagnosis of retroperitoneal tumors, treatment of primary retroperitoneal sarcomas, and management of recurrent or unresectable cases. They also address 11 clinical questions derived from these topics and, for the first time, present a systematic diagnostic and treatment algorithm for this disease—offering important reference value for standardizing the management of retroperitoneal sarcoma in China. The diagnostic process includes assessment of clinical features, imaging evaluation, pathological diagnosis, and biopsy. Despite the technical challenges, surgical resection remains the mainstay of treatment, with a particular emphasis on achieving R0 resection. In addition, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, particle therapy, and targeted therapy also play crucial roles. This article focuses on analyzing and discussing the guideline's recommendations on imaging, pathological diagnosis, and surgical resection, in comparison with other domestic and international guidelines. It further explores the effectiveness of current non-surgical treatment strategies based on recent advances in particle and immunotherapy, and looks ahead to the prospects of improving patient outcomes through personalized treatment, multimodal therapy, and multidisciplinary collaboration.
-
MA Ning, HUANG Haonan, ZHOU Haonan, ZHOU Taicheng, CHEN Shuang
2025,34(4):660-667, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250114
Abstract:
Background and Aims Laparoscopic hiatal hernia repair with mesh reinforcement combined with fundoplication has become the standard surgical approach for treating moderate to severe cases. However, intraoperative and postoperative complications remain a significant concern. This study was conducted to explore the causes of common complications and their prevention and management strategies through retrospectively analyzing clinical data from a single center to optimize perioperative care and improve surgical safety.Methods The clinical data of 432 patients who underwent laparoscopic hiatal hernia repair with mesh and fundoplication at the Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University from January 2018 to December 2023 were retrospectively analyzed. All procedures were performed by the same surgical team using the standardized seven-step protocol for laparoscopic repair. Postoperative care followed the enhanced recovery after surgery pathway. The incidences of intraoperative and postoperative complications were recorded, and univariate analysis was used to identify risk factors for major postoperative complications.Results The overall complication rate was 15.3% among 432 patients. The most common intraoperative complication was bleeding (6.9%), primarily from the inferior phrenic vessels (3.2%), short gastric vessels (1.6%), and parenchymal organ injuries (1.9%). The most frequent postoperative complication was dysphagia (12.0%), followed by pneumothorax (3.2%), hernia recurrence (1.9%), mesh infection or erosion (0.7%), gas-bloat syndrome (6.3%), and gastroparesis (0.9%). Most complications were relieved through conservative treatment, endoscopic dilation, or interventional procedures. Two patients with persistent dysphagia underwent reoperation to remove the fundoplication wrap. The median follow-up period was 34 months, with a 6.0% loss to follow-up rate and no perioperative mortality. Univariate analysis showed that patients aged ≥50 years and those who underwent Nissen fundoplication had significantly higher rates of postoperative dysphagia (both P<0.05).Conclusion Laparoscopic hiatal hernia repair with mesh and fundoplication is generally safe and effective. However, intraoperative vascular injuries and postoperative dysphagia require special attention. Accurate dissection and identification of anatomical layers are critical during surgery. Surgical strategy should be tailored based on patient age and esophageal motility, with partial fundoplication (Toupet or Dor) preferred when appropriate. Combined with enhanced postoperative recovery protocols, standardized mesh placement and fixation can reduce complication rates and improve long-term outcomes.
-
ZHAN Chongwen, LIU Lili, SHEN Qiwei, XU Bo, FU Xiaojian, SHAO Yikai, HUA Rong, YAO Qiyuan
2025,34(4):668-675, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250097
Abstract:
Background and Aims Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a common complication following sleeve gastrectomy (SG), particularly in patients with concomitant hiatal hernia, where symptoms tend to be more persistent and refractory, significantly impairing postoperative quality of life. This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of laparoscopic hiatal hernia repair combined with gastroesophageal fixation in SG patients with severe GERD and hiatal hernia, providing clinical reference for revisional surgical strategies.Methods The clinical data of 9 patients with severe GERD after SG who underwent laparoscopic hiatal hernia repair and gastroesophageal fixation at Huashan Hospital, Fudan University, between January 2023 and June 2024 were retrospectively analyzed. GerdQ scores, proportion of endoscopically confirmed reflux esophagitis, and proton pump inhibitor (PPI) usage were compared before and after surgery. Surgical parameters and follow-up outcomes were also recorded.Results All patients successfully completed the surgery without major intraoperative complications, and the mean postoperative hospital stay was 5.22 d. After a mean follow-up period of 15.27 months, the GerdQ score significantly decreased from 11.67±2.00 to 7.22±1.48. The proportion of patients with GerdQ score≥8 decreased from 100.00% to 44.44%, and the rate of endoscopically confirmed GERD dropped from 88.89% to 11.11%; PPI use also significantly declined, with all differences reaching statistical significance (all P<0.05).Conclusion Laparoscopic hiatal hernia repair combined with gastroesophageal fixation can effectively alleviate reflux symptoms in SG patients with coexisting hiatal hernia, demonstrating favorable short-term efficacy and high safety. This approach may be a preferable surgical option for selected patients.
-
BIAN Shibo, ZHANG Yiqiao, ZHANG Meng, LIU Yang
2025,34(4):676-685, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.240441
Abstract:
Background and Aims Approximately 20%-25% of individuals experience insufficient weight loss (IWL) or weight regain (WR) after bariatric surgery. However, there is limited research on using semaglutide in this patient population, and its efficacy and safety remain to be confirmed. Therefore, this study was conducted to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of semaglutide in patients with IWL or WR after bariatric surgery through a systematic review to provide evidence to support clinical decision-making.Methods A comprehensive search was conducted across multiple domestic and international databases for studies using semaglutide in patients with IWL or WR after bariatric surgery. The search period was from the database's inception to July 1, 2024. Relevant studies were screened according to inclusion and exclusion criteria, and data were analyzed using Stata 14.0 software.Results A total of 5 retrospective studies were included, encompassing 289 patients who received semaglutide treatment after bariatric surgery. The analysis showed that, compared to baseline, semaglutide use resulted in an average total weight reduction of 10.66% (MD=10.66%, 95% CI=6.47%-14.89%); body mass index decreased by 3.57 kg/m2 (MD=3.57 kg/m2, 95% CI=2.46-4.67 kg/m2); the type of surgery did not significantly affect the degree of weight loss (P>0.05). The proportion of patients who experienced >5% weight loss was 80% (OR=0.80, 95% CI=0.76-0.85); >10% weight loss was observed in 45% of patients (OR=0.45, 95% CI=0.41-0.50); and >15% weight loss occurred in 18% of patients (OR=0.18, 95% CI=0.08-0.27). Most patients had undergone sleeve gastrectomy (69.8%). There was no significant difference in HbA1c levels before and after treatment (P>0.05). The incidence of adverse events was 14% (OR=0.14, 95% CI=0.01-0.28), primarily gastrointestinal side effects.Conclusion Semaglutide can significantly reduce body weight in patients with IWL or WR after bariatric surgery, with a relatively low incidence of adverse effects. It may be considered for patients who experience suboptimal weight loss following bariatric surgery. However, further prospective and large-scale clinical studies are needed to confirm these findings.
-
PAN Rongli, ZHAO Peikai, LI Yuxuan, TAO Ruixin, HUANG Xin, LIU Teng, LI Weihua, LIU Shaozhuang
2025,34(4):686-697, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250102
Abstract:
Background and Aims Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common endocrine disorder among obese women, often accompanied by psychological issues such as anxiety and depression. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (LSG) is an effective treatment for obesity and its related metabolic conditions, and has shown clear benefits in improving weight and metabolic profiles in PCOS patients. However, the potential mechanisms by which psychological status may affect weight loss outcomes remain unclear. This study aimed to evaluate the psychological characteristics of obese patients with PCOS and explore their impact on postoperative weight loss outcomes, in order to provide evidence for individualized intervention strategies.Methods Female obese patients scheduled for LSG between November 2020 and September 2022 were enrolled and divided into PCOS and non-PCOS groups. Standardized psychological scales were used to assess anxiety, depression, self-esteem, and eating behaviors. Weight loss outcomes were recorded at 6 and 12 months postoperatively. Propensity score matching was used to control for confounding factors such as age and body mass index (BMI), and correlation analysis was conducted to explore the relationship between psychological status and weight loss outcomes.Results A total of 314 patients were included, with 130 cases (41.4%) in the PCOS group. Before matching, the PCOS group had significantly worse psychological indicators and lower weight loss outcomes compared to the non-PCOS group (all P<0.05); after matching, these differences were no longer statistically significant (all P>0.05). Emotional eating was positively correlated with 12-month weight loss outcomes in the PCOS group, while anxiety and internalized weight stigma were associated with weight loss outcomes in the non-PCOS group (P<0.05). Additionally, among patients with moderate and extreme obesity, weight loss outcomes in the PCOS group were superior to those in the non-PCOS group (P<0.05). BMI was negatively correlated with self-esteem, eating behaviors, and quality of life (all P<0.05).Conclusion Obese patients with PCOS exhibit notable psychological distress. However, after controlling for BMI and age, their psychological status and weight loss outcomes are comparable to those of non-PCOS patients. BMI may serve as an important confounding factor, and psychological factors may influence weight loss indirectly through eating behaviors. Preoperative psychological screening and intervention are recommended.
-
ZHANG Huilin, XU Ting, WANG Chen, ZHANG Hongwei, DI Jianzhong
2025,34(4):698-707, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.240529
Abstract:
Background and Aims Obesity is often accompanied by symptoms of disordered eating. Although bariatric metabolic surgery can alleviate these symptoms, there are significant individual differences in postoperative outcomes, and effective predictive indicators are lacking. Liver and kidney function, along with lipid profiles, are closely related to metabolic status and may serve as useful markers for preoperative risk stratification and prognosis prediction. This study was conducted to explore the relationship between preoperative metabolic indicators and symptoms of disordered eating, thereby identifying postoperative recovery patterns among obese patients to support individualized management strategies.Methods A total of 41 obese patients who underwent sleeve gastrectomy at Shanghai Sixth People's Hospital between September 2020 and June 2023 were enrolled, along with 36 healthy volunteers recruited during the same period. Participants completed the Eating Disorder Inventory-2 (EDI-2) questionnaire, and serum samples were collected to assess liver function, kidney function, and lipid levels prior to surgery. The Mantel test was used to analyze correlations between metabolic indicators and EDI-2 scores. Latent profile analysis (LPA) was conducted using the indicators significantly correlated with EDI-2 scores to identify subgroups within the obese cohort. Linear mixed models were then applied to examine the trajectories of postoperative symptom changes across subgroups.Results Levels of cystatin C, cholinesterase, gamma-glutamyl transferase, triglycerides,and apolipoprotein E were significantly higher in the obese group compared to the healthy group (all P<0.05), and EDI-2 total score was also significantly elevated (P<0.05); the prealbumin level in the healthy group was significantly higher than that in the obese group (P<0.05). These six indicators were positively correlated with EDI-2 score (all r>0.20, P<0.05). Based on these markers, the LPA classified the obese group into two subgroups, with subgroup 2 exhibiting higher levels of most metabolic indicators than subgroup 1. During the 18-month postoperative follow-up, both subgroups showed reductions in EDI-2 score, but symptom improvement in subgroup 2 occurred later (month 6) compared to subgroup 1 (month 4).Conclusion Preoperative levels of cholinesterase, gamma-glutamyl transferase, prealbumin, triglycerides, and apolipoprotein E may serve as predictive indicators for improvement in disordered eating symptoms. Recovery patterns after bariatric surgery vary among obese patients with different metabolic profiles, highlighting the need for tailored intervention strategies.
-
WANG Qian, JIA Tingyin, PENG Chaoyang, LI Yongkun
2025,34(4):708-718, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.240090
Abstract:
Background and Aims The long non-coding RNA SOX2 overlapping transcript (SOX2-OT) is involved in the regulation of cancer cell cycle and proliferation. Bioinformatics analysis has revealed potential binding sites among miR-409-3p, SOX2-OT, and membrane binding protein annexin A2 (ANXA2). This study aims to investigate the expression and functional role of the SOX2-OT/miR-409-3p/ANXA2 axis in gastric cancer cells.Methods qRT-PCR was used to measure the expression levels of SOX2-OT, miR-409-3p, and ANXA2 mRNA in gastric cancer tissues and cell lines. Gastric cancer cells were transfected with SOX2-OT shRNA plasmid (sh-SOX2-OT), co-transfected with sh-SOX2-OT and miR-409-3p inhibitor, or co-transfected with sh-SOX2-OT and ANXA2 overexpression plasmid. The control groups included blank, shRNA-negative control, inhibitor-negative control, and overexpression plasmid-negative control. Expression levels of SOX2-OT, miR-409-3p, and ANXA2 mRNA, cell proliferation, migration/invasion, apoptosis, and protein expression of Ki-67, cleaved caspase-3, Bax, MMP-9, and ANXA2 were assessed. Dual-luciferase reporter assays were conducted to confirm the targeting relationships among miR-409-3p, SOX2-OT, and ANXA2. A xenograft tumor model in nude mice was used to evaluate the effect of SOX2-OT on gastric cancer tumor growth in vivo.Results SOX2-OT and ANXA2 expression levels were significantly upregulated, while miR-409-3p was downregulated in gastric cancer tissues (vs. adjacent non-cancerous tissues) and gastric cancer cell lines (vs. normal gastric epithelial cells) (all P<0.05). In gastric cancer cels, knockdown of SOX2-OT led to decreased expression of SOX2-OT and ANXA2 mRNA and increased expression of miR-409-3p (all P<0.05), and this was accompanied by reduced proliferation and migration/invasion abilities, and increased apoptosis (all P<0.05); protein levels of ANXA2, Ki-67, and MMP-9 were significantly decreased, whereas cleaved caspase-3 and Bax levels were significantly increased (all P<0.05). These effects were reversed by co-transfection with the miR-409-3p inhibitor or ANXA2 overexpression plasmid (all P<0.05). Dual-luciferase assays confirmed the direct targeting relationships among miR-409-3p, SOX2-OT, and ANXA2. In vivo, knockdown of SOX2-OT significantly inhibited tumor growth in nude mice, with reduced SOX2-OT and increased miR-409-3p expression, as well as decreased ANXA2 and Ki-67 protein positivity in xenograft tissues (all P<0.05).Conclusion SOX2-OT is upregulated in gastric cancer cells and may promote malignant behaviors by competitively binding miR-409-3p, thereby relieving its inhibition on ANXA2. The SOX2-OT/miR-409-3p/ANXA2 axis may represent a potential molecular target for gastric cancer therapy.
-
SHANG Qing, WANG Jing, WANG Xiaolei
2025,34(4):719-726, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250092
Abstract:
Background and Aims Valeric acid activates the nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) pathway. Recent studies have demonstrated its potent antitumor activity in breast and oral cancers. However, its role in gastric cancer treatment remains unclear. This study aimed to investigate the effects of valeric acid on inflammatory responses and survival in a gastric cancer xenograft model in nude mice and to explore the potential underlying mechanisms to provide new insights for gastric cancer therapy.Methods A xenograft model was established by subcutaneous injection of human gastric cancer MKN-45 cells into 80 Balb/c nude mice, which were then equally randomized into four groups: control and low-, medium-, and high-dose valeric acid groups (10, 20, and 40 mg/kg, respectively). The mice received daily intraperitoneal injections of either saline or valeric acid for 30 days. Tumor growth was monitored during the treatment period. Twelve hours after the final administration, five mice from each group were sacrificed by cervical dislocation; blood was collected via eyeball removal, and tumors were excised and weighed. Histopathological changes in the tumors were observed by HE staining. Serum levels of macrophage inflammatory protein-2 (MIP-2), interleukin-10 (IL-10), and tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) were measured by ELISA. mRNA and protein expression levels of Nrf2 and its downstream molecules, quinone oxidoreductase-1 (NQO-1) and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), were assessed in tumor tissues using qRT-PCR and Western blot. The remaining 15 mice per group were monitored for survival analysis.Results Compared with the control group, all valeric acid-treated groups showed a significant reduction in tumor volumes at all observation time points and final tumor weight (all P<0.05), with a dose-dependent trend. HE staining revealed densely arranged tumor cells with high cell density in the control group, while various degrees of tumor necrosis and reduced cell density were observed in valeric acid-treated groups, most pronounced in the high-dose group. ELISA results showed that serum levels of MIP-2 and TNF-α were significantly decreased, while IL-10 levels were significantly increased in valeric acid-treated groups compared to controls (all P<0.05), exhibiting dose dependence. qRT-PCR and Western blot analyses demonstrated that the mRNA and protein expression levels of Nrf2, HO-1, and NQO-1 in tumors were significantly elevated in the valeric acid groups compared with the control group (all P<0.05), also showing dose dependence. Survival analysis indicated that the median survival times were 47 d (control), 68 d (low dose), 81 d (medium dose), and 90 d (high dose), with all valeric acid groups having significantly prolonged survival compared to the control group (all P<0.05).Conclusion Valeric acid effectively inhibits the growth of gastric cancer xenografts, attenuates systemic inflammatory responses, and prolongs the survival of nude mice, possibly through activation of the Nrf2 pathway and modulation of the tumor microenvironment.
-
ZHOU Sen, WANG Liwei, WANG Wenhang, ZHENG Hao
2025,34(4):727-734, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.230126
Abstract:
Background and Aims Adhesive intestinal obstruction (AIO) is a type of mechanical bowel obstruction caused by abdominal or intestinal adhesions, and its onset and progression are closely associated with impaired intestinal mucosal barrier function. Danshen injection, a commonly used traditional Chinese medicine preparation with properties of promoting blood circulation and removing blood stasis, has shown therapeutic potential in various gastrointestinal diseases by improving microcirculation and promoting vasodilation. However, its specific mechanism of action in AIO remains unclear. This study was conducted to investigate the effects and potential mechanisms of Danshen injection on intestinal mucosal barrier function in a rat model of AIO.Methods Forty rats with experimentally induced AIO were equally randomized into four groups: the model group (receiving intraperitoneal saline) and three Danshen-treated groups administered low, medium, and high doses of Danshen injection (1, 2, and 4 mL/kg, respectively), once daily for 7 consecutive d. An additional 10 healthy rats received saline injections in the same manner and served as the normal control group. After the final intervention, all rats were euthanized under anesthesia. Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining was performed to evaluate the histopathological morphology of small intestinal tissues. Levels of D-lactic acid and endotoxin in peripheral blood were measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The expression levels of mucin 2 (MUC2), mucin 3 (MUC3), and human defensin 5 (HD5)—key components of the intestinal mucus layer and innate immune response—were analyzed using quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). Colorimetric assays were conducted to assess oxidative stress markers in intestinal tissue, including nitric oxide synthase (NOS), malondialdehyde (MDA), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px). Western blot was used to determine the protein expression levels of endogenous antioxidant pathway components: nuclear factor erythroid 2–related factor 2 (Nrf2), heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), and NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1).Results HE staining showed no significant histological changes in the intestinal tissues of the normal control group, with a mucosal injury score of 0. The model and treatment groups exhibited varying degrees of villous disorganization and tissue edema, with injury scores of 4.69±0.62, 3.36±0.41, 2.29±0.22, and 1.53±0.14 in the model, low-, medium-, and high-dose groups, respectively (all P<0.05 vs. model group). Compared with the normal control group, the other groups showed significantly increased levels of D-lactic acid and endotoxin in the blood (all P<0.05); elevated expression of MUC2 and MUC3, reduced HD5 expression (all P<0.05); increased NOS and MDA levels, decreased SOD and GSH-Px levels (all P<0.05); downregulated expression of Nrf2, HO-1, and NQO1 proteins in intestinal tissues (all P<0.05). These changes were significantly attenuated in the Danshen-treated groups in a dose-dependent manner (all P<0.05).Conclusion Danshen injection can alleviate intestinal mucosal injury in AIO rats, possibly by activating the Nrf2/HO-1/NQO1 signaling pathway and reducing oxidative stress, thereby enhancing the intestinal mucosal barrier function.
-
2025,34(4):735-744, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.240488
Abstract:
Background and Aims Gastric cancer is a common and highly lethal malignancy of the digestive system. The efficacy of current treatment strategies remains limited, highlighting the urgent need to identify novel therapeutic targets. This study employed a Mendelian randomization (MR) approach to integrate GWAS data with pQTL data, aiming to systematically identify and validate plasma proteins that are causally associated with gastric cancer, thereby providing a theoretical basis for targeted therapy.Methods A two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis was conducted using GWAS data on gastric cancer and plasma pQTL datasets to infer causal relationships. External independent datasets were used for validation. Multi-dimensional sensitivity analyses-including reverse causality testing, Bayesian colocalization, and phenome-wide scans-were performed to ensure the robustness of the findings. Protein-protein interaction networks were constructed via the STRING database to elucidate the biological pathways of candidate proteins, and the DrugBank database was utilized to predict potential therapeutic agents.Results A total of 16 plasma proteins were initially identified as causally associated with the risk of gastric cancer. After external validation and sensitivity analyses, ICAM2, IGF1R, LIFR, and MET were confirmed as key candidate targets. Drug database analysis indicated that dalotuzumab (targeting IGF1R) and efalizumab (potentially modulating the ICAM2 pathway) may have therapeutic potential.Conclusion Through a multi-omics Mendelian randomization framework, this study systematically identified four plasma proteins-ICAM2, IGF1R, LIFR, and MET-that exhibit stable causal associations with gastric cancer. These targets offer novel insights into the molecular pathogenesis of gastric cancer and provide a theoretical foundation for developing targeted drugs and personalized treatment strategies.
-
WU Xing'an, LIAO Xinhua, QIU Guanglin, WANG Haijiang, ZHU Mengke, LU Jing, FAN Lin, CHE Xiangming
2025,34(4):745-752, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.240421
Abstract:
Background and Aims Minimally invasive surgery, represented by laparoscopic techniques, plays a vital role in the treatment of gastric cancer. However, postoperative infectious complications remain a key factor affecting patient recovery and prognosis. This study was performed to identify the risk factors associated with early (≤1 month) infectious complications after laparoscopic surgery for gastric cancer, providing a reference for clinical prevention strategies.Methods A retrospective analysis was conducted on 1 572 patients who underwent laparoscopic surgery for gastric cancer at the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University from March 2020 to February 2024. Patients were divided into infection and non-infection groups based on the occurrence of postoperative infectious complications. Univariate and multivariate Logistic regression analyses were performed to identify related risk factors.Results Among the 1 572 patients, 194 cases (12.3%) developed early postoperative infectious complications, including intra-abdominal infections (4.1%), surgical site infections (3.7%), and pulmonary infections (5.6%). Univariate analysis revealed that a history of diabetes, pulmonary disease, smoking, and preoperative anemia and hypoalbuminemia were significantly associated with postoperative infections (all P<0.05). Multivariate analysis indicated that a history of diabetes (OR=6.927, 95% CI=4.194-12.935), smoking (OR=3.079, 95% CI=2.261-4.913), and preoperative albumin <35 g/L (OR=0.572, 95% CI=0.302-1.578) were independent risk factors for early postoperative infectious complications.Conclusion A history of diabetes, smoking, and preoperative hypoalbuminemia are closely associated with the occurrence of early postoperative infectious complications after laparoscopic gastric cancer surgery. Clinical attention should be paid to perioperative metabolic, nutritional, and lifestyle management, and early intervention for high-risk patients may help reduce the incidence of complications, improve recovery, and enhance treatment outcomes.
-
2025,34(4):753-759, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.240181
Abstract:
Background and Aims Intestinal obstruction is a common acute abdominal condition, and early diagnosis and timely surgical intervention are critical to patient prognosis. After radical gastrectomy for gastric cancer, due to abnormal digestive tract reconstruction, mesenteric space formation, and peritoneal injury, the incidence of intestinal obstruction is relatively high, often accompanied by ascites of varying characteristics. Bloody ascites usually suggest intestinal wall ischemia and necrosis; however, current clinical indicators have limited effectiveness in the early identification of this condition. This study was performed to investigate the clinical characteristics of postoperative small bowel obstruction with different types, with a particular focus on identifying markers with diagnostic values for bloody ascites.Methods The clinical data of 65 patients with small bowel obstruction and ascites after radical gastrectomy for gastric cancer admitted to the Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery of Jiangyin People's Hospital between January 2010 and December 2021 were retrospectively analyzed. Based on the ascites characteristics, patients were divided into serous ascites group (n=42), chylous ascites group (n=9), and bloody ascites group (n=14). Clinical parameters and preoperative white blood cell count (WBC), neutrophil count (NEU), lymphocyte count, and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) were compared among the groups. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was used to evaluate the diagnostic value of inflammatory markers for bloody ascites.Results The time from onset to hospital admission was significantly longer in the serous ascites group compared to the chylous and bloody ascites groups (P<0.05). Postoperative hospital stay was significantly prolonged in the bloody ascites group compared to the other two groups (P<0.05). The rate of small bowel resection in the bloody ascites group (6/14) was significantly higher than that in the chylous ascites group (0/9) or serous ascites group (7/42) (P<0.05). Although the recurrence rate in the bloody ascites group (3/14) was higher than in the chylous ascites group (1/9) or serous (2/42) ascites group, the difference was not statistically significant (P>0.05). WBC, NEU, and NLR levels increased progressively from the serous to chylous to bloody ascites groups, with statistically significant differences (P<0.05). ROC curve analysis showed that NLR had superior diagnostic performance in predicting bloody ascites (AUC: 0.84; sensitivity: 75%; specificity: 85%) compared to WBC and NEU.Conclusion NLR is closely associated with the characteristics of ascites in patients with small bowel obstruction after radical gastrectomy and is significantly elevated in those with bloody ascites. Compared to traditional inflammatory markers WBC and NEU, NLR demonstrates higher sensitivity and specificity for identifying bloody ascites, making it a valuable adjunct diagnostic tool for predicting intestinal wall ischemia and necrosis. Furthermore, patients with bloody ascites showed higher rates of bowel resection and more extended hospital stays, suggesting a poorer clinical prognosis.
-
QIU Xiaoyuan, ZHOU Jiaolin, LIN Guole, LU Junyang, NIU Beizhan, QIU Huizhong
2025,34(4):760-768, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.240110
Abstract:
Background and Aims For patients with mid-to-low rectal cancer who achieve clinical complete response (cCR) or near-cCR after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (nCRT), the key concern for both clinicians and patients is how to preserve anal function as much as possible without significantly compromising oncological outcomes. This study was performed to evaluate the safety and feasibility of local excision as an anus-preserving approach in rectal cancer patients with cCR or near-cCR.Methods A retrospective analysis was conducted on 51 patients with mid-to-low rectal cancer who underwent local resection after achieving cCR or near-cCR following nCRT at Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, between March 2014 and July 2023. The clinical characteristics, imaging and pathological findings, surgical outcomes, as well as oncological and functional results were reviewed.Results Among the 51 patients, 34 were male and 17 were female, with a mean age of 61±14 years. Pre-nCRT imaging staging showed: cT1-2N0 in 12 cases (23.5%), cT3N0 in 13 cases (25.5%), cT1-3N0-1 in 19 cases (37.4%), and cT1-3N2 in 7 cases (13.7%). The average tumor distance from the anal verge was (4.5±1.1) cm. After achieving cCR or near-cCR following nCRT, all patients underwent local resection: 40 cases (78.4%) underwent transanal endoscopic microsurgery (TEM), 7 cases (13.7%) underwent transanal minimally invasive surgery (TAMIS), and 4 cases (7.8%) underwent conventional transanal local excision. The postoperative complication rate was 27.5% (14/51), with 71.4% classified as Clavien-Dindo grade I. Postoperative histopathology showed ypT0 in 26 cases (51.0%), ypT1 in 8 cases (15.7%), ypT2 in 16 cases (31.4%), and ypT3 in 1 case (2.0%). The concordance rate between pathological results and preoperative imaging was 54.9%. Over a median follow-up of 60 months (range: 34-79), there were 4 cases (7.8%) of local recurrence, 12 cases (23.5%) of distant metastasis, and 5 cancer-related deaths (9.8%). Six months postoperatively, both the Wexner score and the low anterior resection syndrome (LARS) score significantly improved compared to post-nCRT values [Wexner: 1 (0-2) vs. 2 (1-5); LARS: 3.3±5.75 vs. 4.3±6.86; both P<0.01].Conclusion For patients with mid-to-low rectal cancer who achieve cCR or near-cCR after nCRT, local en bloc resection of the bowel wall lesions enables accurate assessment of residual tumor status and facilitates personalized subsequent treatment, potentially sparing some patients from radical surgery. Local resection can be a viable anus-preserving option for patients who are unfit for or strongly averse to radical resection. However, local excision cannot replace radical surgery, and its precise indications warrant further investigation.
-
LI Lei, LUO Dakui, XU Nan, WANG Yanjun, LIAN Peng, LI Xinxiang
2025,34(4):769-777, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.240379
Abstract:
Background and Aims According to the Chinese Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Colorectal Cancer (2023 Edition), patients with early-stage colorectal cancer who present with high-risk factors require additional radical surgery following endoscopic resection. However, due to the relatively low rate of lymph node metastasis in early colorectal cancer, some patients may not benefit from such supplemental surgery. Therefore, accurately identifying patients who are truly likely to benefit and refining the indications for supplemental surgery are pressing clinical challenges. This study was conducted to investigate the risk factors and distribution patterns of lymph node metastasis following additional radical surgery through retrospectively analyzing a large single-center cohort, thereby providing evidence-based support for clinical decision-making.Methods Clinicopathologic data were retrospectively reviewed for patients with early-stage colorectal cancer who underwent additional radical surgery at Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center between 2008 and 2023. Binary Logistic regression and multivariate analyses were performed to identify risk factors associated with lymph node metastasis, and the distribution characteristics of metastatic lymph nodes were further examined.Results A total of 417 patients were included in the study, with lymph node metastasis confirmed in 36 cases (8.63%) postoperatively. Over time, the number of patients undergoing supplemental surgery increased, while the proportion of cases with residual cancer decreased. Among 243 patients included in the risk factor analysis, univariate analysis indicated that submucosal invasion depth of SM2 or greater, poor tumor differentiation, positive vascular invasion, and tumor location were high-risk factors for lymph node metastasis. Multivariate analysis identified invasion depth (P=0.039) and tumor location (P=0.014) as independent risk factors. Among the metastatic cases, 58.3% involved a single lymph node; 63.9% of metastases were limited to the first station, and 36.1% extended to the second station, with no metastasis found at the third station. Only four patients had preoperative imaging suggestive of lymph node enlargement.Conclusion Although the number of supplemental surgeries following endoscopic resection of early-stage colorectal cancer has increased significantly, the actual rate of lymph node metastasis remains low, suggesting a potential risk of overtreatment. Submucosal invasion depth ≥SM2 and tumor location are independent risk factors for metastasis. D2 lymph node dissection is deemed necessary, while the diagnostic value of imaging remains limited. Clinical decisions should prioritize precision and individualized treatment planning.
-
YIN Shaojun, YANG Hailong, WANG Guixian, LI Zhen, YUAN Weitang, XIA Kunkun
2025,34(4):778-786, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250080
Abstract:
Background and Aims Complete situs inversus (SIT) is a rare congenital abnormality of organ mirror-image arrangement, presenting certain challenges for abdominal surgical procedures. The Da Vinci robotic system, with its high-definition 3D vision and flexible operation, holds potential for application in patients with anatomical variations. This report presents the diagnosis and treatment process of a patient with rectal mass and SIT who underwent robotic-assisted surgery. Additionally, relevant literature is reviewed to provide insights for individualized surgical strategies in patients with complex anatomical variations and to promote the further clinical application of robotic-assisted surgery systems.Methods A case from the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University is reported, in which a patient with rectal mass and SIT successfully underwent lesion resection using the Da Vinci robotic system with an unconventional "five-port" technique. A systematic literature review was also conducted (including 35 case reports), to summarize the surgical characteristics of colorectal procedures in SIT patients and the advantages of robotic system application.Results The patient was a 74-year-old male who presented with rectal bleeding. Imaging confirmed the diagnosis of SIT, and colonoscopy revealed a large polypoid mass with ulceration at the apex, located 13-18 cm from the anal verge. The patient subsequently underwent Da Vinci robotic-assisted resection of the rectal lesion. The robotic system effectively overcame the challenges posed by mirror-image anatomy, enabling complete excision of the lesion. The operation lasted 183 minutes, with intraoperative blood loss of less than 20 mL. Postoperative pathology confirmed a villous tubular adenoma with high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia. The patient had an uneventful recovery, and no recurrence was observed during the 9-month follow-up. Literature analysis demonstrated that the robotic system, through magnified 3D visualization, flexible instrument articulation, and tremor filtration, significantly improves surgical precision in patients with anatomical anomalies.Conclusion The Da Vinci robotic system effectively addresses the challenges of anatomical variations related to SIT in low rectal surgery. Its stability and precision offer a new technical option for tumor resection under complex anatomical conditions, demonstrating clinical value for widespread application.
-
2025,34(4):787-795, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250049
Abstract:
Mucinous gastric adenocarcinoma (MGC) is a distinct but under-researched subtype of gastric cancer, accounting for approximately 2.2% to 6.8% of all cases. It is characterized by the presence of ≥50% extracellular mucin within the tumor tissue. Although recognized as an independent subtype by international classification standards, significant controversies persist regarding the definition criteria, clinical prognosis, and treatment strategies of MGC. This article systematically reviews the epidemiological features, histological evolution, molecular mechanisms, and imaging characteristics of MGC, with a particular focus on the key issues related to definitional discrepancies, prognostic contradictions, and therapeutic challenges. Addressing these issues may provide references for optimizing clinical diagnosis and treatment, promote the development of individualized therapeutic strategies for MGC, and offer theoretical support for reducing global disparities in gastric cancer management.
-
2025,34(4):802-809, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.240194
Abstract:
背景与目的 结直肠癌是全球发病率第三的常见恶性肿瘤,且多数患者在确诊时已处于中晚期,预后较差,临床亟须寻找新的分子靶点以提高诊疗效果。血管扩张刺激磷蛋白(VASP)、环氧化酶2(COX-2)和程序性死亡配体1(PD-L1)在多种恶性肿瘤中被证实与肿瘤进展和免疫逃逸密切相关,但其在结直肠癌中的表达特征及临床意义尚不明确。本研究探讨VASP、COX-2和PD-L1在人结直肠癌组织中的表达及其临床意义,以期为结直肠癌的诊断和预后评估提供新思路。方法 收集2017年6月─2020年12月湖北省咸宁市中心医院96例行结直肠癌根治术的患者为研究对象,分别用qRT-PCR和免疫组化分析VASP、COX-2、PD-L1在结直肠癌组织中的表达及其与患者临床病理因素、预后的关系。结果 qRT-PCR结果显示,结直肠癌组织中VASP、COX-2、PD-L1的mRNA表达水平均明显高于癌旁组织(均P<0.05);在结直肠癌组织中,VASP和COX-2的mRNA表达呈正相关,COX-2和PD-L1的mRNA表达呈正相关(均P<0.05);VASP、COX-2、PD-L1的mRNA表达是结直肠癌的危险因素(均P<0.05)。免疫组化结果显示,淋巴结转移、肿瘤分化程度、临床分期与VASP、COX-2、PD-L1表达程度有关,肿瘤浸润程度与COX-2表达程度有关(均P<0.05);VASP、COX-2、PD-L1低表达患者生存率高于各自高表达患者(均P<0.05);淋巴结转移、肿瘤分化程度、临床分期、COX-2和PD-L1表达是结直肠癌患者总生存时间的独立危险因素(均P<0.05)。结论 VASP、COX-2及PD-L1在结直肠癌组织中高表达,三者可能协同参与肿瘤的发生与进展。它们的表达水平不仅与患者的临床病理特征密切相关,亦可作为潜在的预后评估指标,为结直肠癌的分子分型与个体化治疗提供参考依据。
Volume 34,2025 Number 4
GUIDELINE AND CONSENSUS
COMMENTARY
MONOGRAPHIC SYMPOSIUM
INTERPRETATION OF GUIDELINES
MONOGRAPHIC STUDY
BASIC RESEARCH
CLINICAL RESEARCH
REVIEW
BRIEF ARTICLES
-
ZHAO Yu, ZHAO Jichun, ZHANG Lan, HUANG Jianhua, GUO Pingfan, WANG Tao, LI Yongjun, WANG Haiyang, CHEN Quan, Peripheral Vascular Disease Management Branch of the Chinese Geriatric Society
Abstract:
The incidence of chronic venous disease (CVD) is significantly higher in the elderly population compared to non-elderly individuals, with more severe disease manifestations. Additionally, elderly CVD patients often have comorbid conditions such as cardiovascular diseases, making the evaluation process more complex and increasing treatment difficulty. Currently, there are no established recommendations in China for the diagnosis and treatment of CVD in individuals aged 60 and above. Against this backdrop, the Peripheral Vascular Disease Management Branch of the Chinese Geriatric Society has developed the Chinese Expert Consensus on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Chronic Venous Disease in the Elderly based on domestic and international guidelines, relevant evidence-based medical research, and the physiological and clinical characteristics of the elderly population in China. This consensus aims to provide an important reference for improving the diagnosis and treatment of CVD in elderly patients in China.